Android Bluetooth接続
I. 概要
Bluetoothは、固定機器、モバイル機器、ビルディングパーソナルネットワークの間で近距離のデータ交換を可能にする無線技術規格である。最大7台のBluetooth機器と同時に接続し、通信を行うことができる。Bluetoothは、従来のBluetooth(Bluetooth 3.0仕様以前)と低電力Bluetooth(Bluetooth 4.0仕様以降)に大別される。
Androidはバージョン4.3(API Level 18)からBluetooth Low Energy(BLE)通信に対応し、アプリがBluetooth機器のスキャン、ペアリング、接続、データ転送を行うためのAPIが提供されています。
Android BLE API には、いくつかの重要なクラスがあります。
1. BluetoothAdapter
ローカルのBluetoothアダプタです。すべての Bluetooth インタラクション操作のエントリポイントです。このクラスでは、他の Bluetooth デバイスの検出、ペアリング済みデバイスのリストの照会、既知の MAC アドレスによる BluetoothDevice のインスタンス化、および他のデバイスとの通信をリッスンするための BluetoothServerSocket の作成を行うことができます。
2. BluetoothDevice
リモートのBluetoothデバイスです。このクラスを使用して、リモートデバイスへの BluetoothSocket 接続を要求したり、デバイス名、アドレス、クラス、および接続ステータスなどのデバイス情報を問い合わせたりします。
3. BluetoothSocket
Bluetoothソケット(TCPソケットに類似)のインターフェイスを表します。アプリケーションがInputStreamとOutputStreamを介して他のBluetoothデバイスとデータを交換するための接続ポイントです。
4. BluetoothServerSocket
は、リクエストを受け付けるオープンなサーバーソケットを表します(TCP ServerSocketに似ています)。2つのAndroidデバイスを接続するには、デバイスがこのクラスを使ってサーバーソケットを開く必要があります。リモートのBluetoothデバイスがそのデバイスへの接続要求を開始すると、BluetoothServerSocketは、接続を受け入れる接続済みBluetoothSocketを返します。
III. Bluetoothの開発
1. プロセス
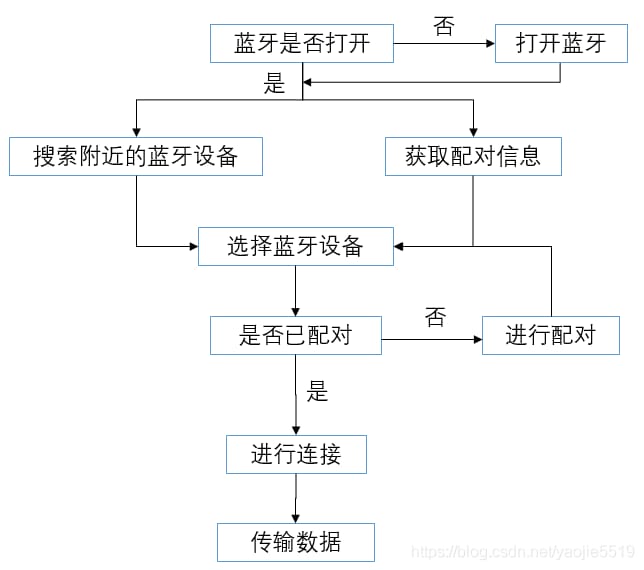
2. パーミッションをオンにする
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH"/>
//When Bluetooth is enabled, mBluetoothAdapter.enable() requires the following permissions
<use-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN"/>
3. Bluetoothをオンにする
public void isBluetoothEnable() {
//Get the Bluetooth adapter
mBluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
if (mBluetoothAdapter ! = null){
// Bluetooth is turned on
if (mBluetoothAdapter.isEnabled()){
}else{// If not open, then open, here you can prompt user to open by popup box
mBluetoothAdapter.enable()
}
}
}
4. 近くのBluetoothデバイスを検索する
/**
* Register to search for broadcasts of Bluetooth devices
*/
private void startDiscovery() {
IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter(BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND);
registerReceiver(receiver, filter);
IntentFilter filter1 = new IntentFilter(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_DISCOVERY_FINISHED);
registerReceiver(receiver, filter1);
startScanBluetooth();
}
private void startScanBluetooth() {
// Determine if it is searching, if it is searching, cancel the search
if (bluetoothAdapter.isDiscovering()) {
bluetoothAdapter.cancelDiscovery();
}
// Start the search
bluetoothAdapter.startDiscovery();
}
/**
* Bluetooth radio reception
*/
private final BroadcastReceiver receiver = new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String action = intent.getAction();
if (BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND.equals(action)) {
BluetoothDevice device = intent.getParcelableExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_DEVICE);
// Bluetooth rssi parameter, represents Bluetooth strength
short rssi = intent.getExtras().getShort(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_RSSI);
//Bluetooth device name
String name = device.getName();
//state of the device
int status = device.getBondState();
...
} else if (action.equals(BluetoothDevice.ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED)) {
...
} else if (BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_DISCOVERY_FINISHED.equals(action)) { ...
Toast.makeText(context, "Bluetooth device search complete", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
};
Bluetoothの接続状態について。
BluetoothDevice.BOND_BONDED: ペアリング済み
BluetoothDevice.BOND_BONDING: ペアリング進行中
BluetoothDevice.BOND_NONE:ペアリングしていない、またはペアリングを解除している
Bluetoothの強度rssiについて。
単位はdbm、Bluetooth信号の強さRSSI = 10*log P、Pは受信信号電力を表します。Bluetoothはブロードキャストを送信し、距離の大きさは、信号の電力強度に影響を与えます。送信電力が最大値の1mwを取るとして、RSSIの値は0、つまりBluetoothに最も近づいた時に得られるRSSIの値は理想的な状態では0ですが、実際にはそのような理想的な状態は基本的にないので、RSSIの値は基本的に負の数になっています。
一般にBLEでは、信号強度を強、中、弱、弱の4段階に分けていると仮定すると、rssiの範囲は順に-60~0 , -70~60 , -80~70 , <~80となります。
5. ペアリング
//Get paired device information
public List<BluetoothDevice> getPairedBluetoothDevices() {
List deviceList = new ArrayList<>();
Set<BluetoothDevice> pairedDevices = mBluetoothAdapter.getBondedDevices();
if (pairedDevices.size() > 0) {
for (BluetoothDevice device : pairedDevices) {
deviceList.add(device);
}
}
return deviceList;
}
//If the number of paired devices is 0, jump to the phone system Bluetooth settings interface
Intent enableBtIntent = new Intent(Settings.ACTION_BLUETOOTH_SETTINGS);
mContext.startActivity(enableBtIntent);
//Manual pairing, just rescan when done
Method method = BluetoothDevice.class.getMethod("createBond");
method.invoke(itemlist.get(position).getDevice());
public class BluetoothConnectThread extends Thread {
private static final UUID BluetoothUUID = UUID.fromString("0000001101-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FB");
BluetoothSocket bluetoothSocket;
BluetoothDevice bluetoothDevice;
private boolean connected = false;
private Object lock = new Object();
// Bluetooth connection callback interface
private BluetoothConnectCallback connectCallback;
public BluetoothConnectThread(BluetoothDevice device,
BluetoothConnectCallback callback) {
try {
bluetoothDevice = device;
bluetoothSocket = bluetoothDevice.createInsecureRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(BluetoothUUID);
connectCallback = callback;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
if (bluetoothSocket ! = null) {
if (connected) {
cancel2();
connected = false;
}
}
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
connect();
if (connected) {
if (connectCallback ! = null){
connectCallback.connectSuccess(bluetoothSocket);
}
}
}
}.start();
}
public void connect() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
bluetoothSocket.connect();
connected = true;
connected = true; }
} catch (Exception connectException) {
connectException.printStackTrace();
cancel();
try {
Method m;
m = bluetoothDevice.getClass().getMethod("createRfcommSocket", new Class[]{int.class});
bluetoothSocket = (BluetoothSocket) m.invoke(bluetoothDevice, Integer.valueOf(1));
bluetoothSocket.connect();
connected = true;
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
if (connectCallback ! = null){
connectCallback.connectFailed(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
public void cancel() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
if (connected) {
bluetoothSocket.close();
connected = false;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
public void cancel2() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
bluetoothSocket.close();
connected = false;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
public interface BluetoothConnectCallback {
void connectSuccess(BluetoothSocket socket);
void connectFailed(String errorMsg);
void connectCancel();
}
//Get the output stream of BluetoothSocket
OutputStream outputStream = bluesocket.getOutputStream();
//then write the data to the output stream to complete the transfer
outputStream.write(data);
outputStream.flush();
6. 接続
Bluetooth接続はサブスレッドで行う必要があります。
public class BluetoothConnectThread extends Thread {
private static final UUID BluetoothUUID = UUID.fromString("0000001101-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FB");
BluetoothSocket bluetoothSocket;
BluetoothDevice bluetoothDevice;
private boolean connected = false;
private Object lock = new Object();
// Bluetooth connection callback interface
private BluetoothConnectCallback connectCallback;
public BluetoothConnectThread(BluetoothDevice device,
BluetoothConnectCallback callback) {
try {
bluetoothDevice = device;
bluetoothSocket = bluetoothDevice.createInsecureRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(BluetoothUUID);
connectCallback = callback;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
if (bluetoothSocket ! = null) {
if (connected) {
cancel2();
connected = false;
}
}
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
connect();
if (connected) {
if (connectCallback ! = null){
connectCallback.connectSuccess(bluetoothSocket);
}
}
}
}.start();
}
public void connect() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
bluetoothSocket.connect();
connected = true;
connected = true; }
} catch (Exception connectException) {
connectException.printStackTrace();
cancel();
try {
Method m;
m = bluetoothDevice.getClass().getMethod("createRfcommSocket", new Class[]{int.class});
bluetoothSocket = (BluetoothSocket) m.invoke(bluetoothDevice, Integer.valueOf(1));
bluetoothSocket.connect();
connected = true;
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
if (connectCallback ! = null){
connectCallback.connectFailed(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
public void cancel() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
if (connected) {
bluetoothSocket.close();
connected = false;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
public void cancel2() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
bluetoothSocket.close();
connected = false;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
public interface BluetoothConnectCallback {
void connectSuccess(BluetoothSocket socket);
void connectFailed(String errorMsg);
void connectCancel();
}
上記に注意、BluetoothUUIDは概ね固定、connect()は接続成功率向上のためサブスレッドに配置(不明)、接続失敗はcreateRfcommSocket thisメソッドを反映する必要があるので注意、現状セルフチェックの方が接続成功率が高いです。
7. データ転送
//Get the output stream of BluetoothSocket
OutputStream outputStream = bluesocket.getOutputStream();
//then write the data to the output stream to complete the transfer
outputStream.write(data);
outputStream.flush();
関連
-
第20章 OnCheckedChangeListenerイベント (ゼロから学ぶAndroid)
-
ADBサーバーがACKしなかった
-
jniとjavaの間でbytearrayを受け渡しする
-
Android StudioでJavaファイルが認識されない問題を解決(赤いJが表示される)。
-
Android LayoutInflaterの原則の分析は、ビュー(a)のステップの深い理解によってあなたのステップを取る
-
java.lang.SecurityException を解決してください。android パッケージは 10065 に属していません。
-
Android用ニュースアプリの簡単な実装です。
-
android.content.res.Resources$NotFoundException: 文字列リソースID #0x1
-
android.content.res.Resources$NotFoundException: 文字列リソースID #0x1エラー
-
Android AVDで "このターゲットにはシステムイメージがインストールされていません "と表示される
最新
-
nginxです。[emerg] 0.0.0.0:80 への bind() に失敗しました (98: アドレスは既に使用中です)
-
htmlページでギリシャ文字を使うには
-
ピュアhtml+cssでの要素読み込み効果
-
純粋なhtml + cssで五輪を実現するサンプルコード
-
ナビゲーションバー・ドロップダウンメニューのHTML+CSSサンプルコード
-
タイピング効果を実現するピュアhtml+css
-
htmlの選択ボックスのプレースホルダー作成に関する質問
-
html css3 伸縮しない 画像表示効果
-
トップナビゲーションバーメニュー作成用HTML+CSS
-
html+css 実装 サイバーパンク風ボタン
おすすめ
-
呼び出しは、ユーザーによって拒否される可能性のある許可を必要とします。
-
Android studio java ファイル表示 j burst red
-
ArrayAdapter のソリューションでは、リソース ID が TextView である必要があります。
-
AndroidでSPAN_EXCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVEスパンが長さ0にできない場合、EditTextでコンテンツを削除する
-
Androidリストウィジェット開発詳細
-
ConstraintLayoutにおけるChainとGuidelineの利用について
-
android:paddingとandroid:marginの違いについて。
-
android ImageViewの割り当て問題 setImageResourceとsetImageBitmap
-
Androidアプリ】【形状利用概要
-
java.util.Iterator java.util.List.iterator()' で null オブジェクト参照例外が発生した場合の解決策を紹介します。