matplotlib.pyplotの軸
2022-02-25 01:54:14
基本的な考え方
matplotlib.pyplotで
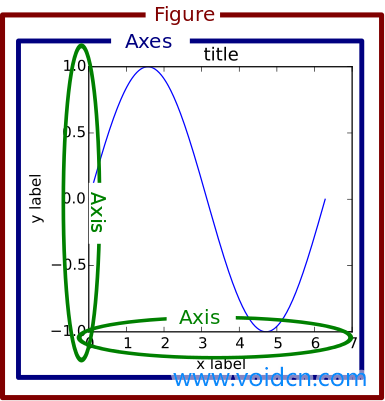
図は白紙の画板である
画板の上 軸(アックス)を持つセット は、その セット要素 は、リージョンを定義する基本的な2軸を含む
パレットの各領域を変更するだけで、もちろんデフォルトでリージョンになっています
そしてサブプロット サブプロットは、実は軸の特殊なケース(サブセット)なのです 明らかにいくつかの軸を取得し、特定の場所に絞り込むことはサブです
<ブロッククオートほとんどの人はサブプロットに慣れていると思いますが、これはサブプロットインスタンスの通常の行×列のグリッドに住むAxesの特別なケースに過ぎません。もし、任意の場所に Axes を作成したい場合は、単に 追加_axes() このメソッドは、0-1の相対的な図座標で[left, bottom, width, height]の値のリストを受け取ります。
基本操作
現在のコンフィグレーションの取得
fig1=plt.figure()
軸となるフィールドの設定
ax1 = plt.Axes(fig1,[0.2, 0.2, 0.4, 0.4])
図に軸フィールドを追加する
fig1.add_axes(ax1)
図にサブグラフを追加し、オブジェクトを保持する
ax3=fig1.add_subplot(224) #Obviously subplot does not have the general axis field set in the previous step
基本タイプ
fig1:
class 'matplotlib.figure.Figure'
ax1です。
class 'matplotlib.axes._axes.
ax3です。
class 'matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot'
パッチモジュール(4つの基本グラフ)

詳細はコードコメント参照
コード例
#Deeper understanding of axes
#An axes is equivalent to a plotting region distributed on a large canvas fig
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import patches
import numpy as np
import cv2
from pylab import *
fig1 = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5)) # in inches!
ax1 = plt.Axes(fig1,[0.2, 0.2, 0.4, 0.4]) # come to an axis in fig1
#ax.set_axis_off()# remove axes
fig1.add_axes(ax1)#add to fig
ax2 = plt.Axes(fig1,[0.4, 0.4, 0.4, 0.4])# one more axis, in fig1
fig1.add_axes(ax2)#add to fig
print(type(ax1),type(ax2))#observe the type
'''
If I want to add "subplot" directly, it seems that if I use subplot directly, it will draw it directly and overwrite the non-subplot axes in the previous canvas
I can use the add method of fig to add it directly, so it won't overwrite the
'''
# ax3=plt.subplot(224)# will clear the rest of the non-subplot axes
ax3=fig1.add_subplot(224)#will not clear the canvas, the previous axes at the specified position will remain
#plt.subplot(221)#default will draw to the current fig, but the previous specified position of the axes cleared
ax4=fig1.add_subplot(221)#will not clear the canvas, the previous specified location of the axes remain
print(type(ax3),type(ax4))#watch type
# the following four drawing areas in ax1,2,3,4 respectively
x=np.range(0,40*pi,0.001)
y=10*np.cos(x)
ax1.plot(x,y,'r--')
ax2.plot(y,x,'b')
ax3.plot(x,y,'g')
ax4.plot(y,x,'y')
# test the image in ax4
img=cv2.imread(r'E:\my_nut_yun\mycode_python\Image Playground\Chrysanthemum.jpg',0)#Grayscale mode
ax4.imshow(img,cmap='gray',aspect="auto")
ax4.plot([0,300],[0,300],'y',linewidth=10)#draw a line
ax4.set_title('test image')
# s=ax4.get_title() # get its title str type
# print(type(s))
ax5 = fig1.add_subplot(443)
mu, sigma = 100, 15
x = mu + sigma * np.random.randn(1000000) # ~N(0,1)
# divide x into bins according to its range count the number of occurrences of each hist graph
n, bins, patchess=ax5.hist(x, 50, color='g', alpha=0.4,normed=True)#alpha is the transparency normed makes the vertical coordinate is the probability
ax5.set_xlabel('Smarts')
ax5.set_ylabel('Probability')
ax5.set_title('Histogram of IQ')
ax5.text(60, .025, r'$\mu=100,\\sigma=15$')
ax5.grid(True)
binbin=[]
for i in range(len(bins)-1):
binbin.append((bins[i]+bins[i+1])/2)
#print(binbin)# new value of the horizontal coordinate Take the midpoint of two adjacent
#print(patchess[0]) #rectangles object can be iterated
ax5.plot(binbin,n,'r--')
patchess[25].set_color('r')
ax5.add_patch(patchess[25])
# test patches
ax6=fig1.add_subplot(3,3,7)
Rectangle((20,20),20,20,linewidth=3, edgecolor='b', facecolor='r')
circle = patches.Circle((50,50), 10, color = "r")
Ellipse((0,0), 18, 24, color= "y") # circle center long diameter short diameter
polygon = patches.RegularPolygon((80,80), 6,20 , color= "b") #Polygon: center Number of sides "radius"
ax6.add_patch(rec)
ax6.add_patch(circle)
ax6.add_patch(ellipse)
ax6.add_patch(polygon)
ax6.set_xlim(0,100)
ax6.set_ylim(0,100)
ax6.axis("equal")
show()
成果

関連
-
Python3.3継続行のアンダーインデントで、.の後に複数のスペースを入れて視覚的にインデントしています。
-
pip AttributeError: 'module' オブジェクトには 'SSL_ST_INIT' という属性がありません。
-
PyQt5演習:matplotlibでプロットする
-
print'の呼び出しに括弧がない Python for Beginners
-
ModuleNotFoundError: numpy.testing.decorators'という名前のモジュールがありません。
-
python-OverflowError: Python の int が大きすぎるため C の long に変換できない
-
TypeError: バイトライクオブジェクトで文字列パターンを使用できない
-
jupyter notebookのアンインストールで "The jupyter" distribution was not found 問題が発生する。
-
ガールフレンドが深夜12時に彼女をベッドに急がせるよう頼んだが、私はそれをしないパイソンを持っています。
-
タオバオ販売(特定値表示可能)インターフェイス
最新
-
nginxです。[emerg] 0.0.0.0:80 への bind() に失敗しました (98: アドレスは既に使用中です)
-
htmlページでギリシャ文字を使うには
-
ピュアhtml+cssでの要素読み込み効果
-
純粋なhtml + cssで五輪を実現するサンプルコード
-
ナビゲーションバー・ドロップダウンメニューのHTML+CSSサンプルコード
-
タイピング効果を実現するピュアhtml+css
-
htmlの選択ボックスのプレースホルダー作成に関する質問
-
html css3 伸縮しない 画像表示効果
-
トップナビゲーションバーメニュー作成用HTML+CSS
-
html+css 実装 サイバーパンク風ボタン
おすすめ
-
ユニコード・オブジェクトは、ハッシュ・エラーの解決前にエンコードする必要があります。
-
Python は '' で '__main__' モジュールを見つけることができません。
-
'dict' オブジェクトには 'has_key' という属性がありません。
-
Python|ModuleNotFoundErrorを解決する。utils' という名前のモジュールがありません。
-
ModuleNotFoundError: _pywrap_tensorflow_internal'という名前のモジュールはありません。
-
TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' オブジェクトが呼び出し可能でないエラー処理
-
OperationalError: データベースファイルを開くことができない Solution
-
Pythonで問題解決。TypeError: 'encoding' is an invalid keyword argument for this function.
-
Python2.7のエンコード問題:UnicodeDecodeError: 'ascii' codec can't decode byte 0xe8 in position... 解決方法
-
AttributeError:partially initialized module ''has no attribute'' (most likely dueto a circular import)