Postgresqlの高度なアプリケーションは、セルのアイデアをマージするの詳細
1. 前に書く✍」。
前回の記事に続き postgresql 高度な行から列への適用と要約のまとめ もう一歩踏み込んで、もっと複雑なことをやってみたい(チャートはとりあえず置いといて ? もちろん、レポートとして、一番多いのはセルの結合です、はい、待ち遠しいです ? ~
2. 考える
まず、フロントエンドの説明を頭の中に入れておきます。
table
もちろん、これはフロントエンド以外の学生には非常に不親切なので、もしあなたが以下を読もうとして困っているなら(フロントエンドの
html
, , および
javascript
) はここで止めることができます。
enn... フロントエンドを少し説明します。
html
表形式の?
2.1 フロントエンド
html
->
table
基本構造
まず、非常に基本的なhtmlを与えてみましょう。
demo.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<! -- This defines two attributes border:defines the table border cellpadding:defines the cell size -->
<table border="3" cellpadding="8">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>tablehead1</th><th>tablehead2</th><th>tablehead3</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>1st row 1st</td><td>1st row 2nd</td><td>1st row 3rd</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<! -- Use the colspan attribute for horizontal merging, the position of the horizontal merged cell needs to be freed up -->
<! -- The following horizontal merging of two cells, so the second td tag should not be written, otherwise it will overflow Oh ~ -->
<td colspan="2"> horizontally merged two cells </td><td> second line 3rd </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>3rd row 1st</td><td>3rd row 2nd</td><td>3rd row 3rd</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<! -- Vertical merge using the rowspan attribute, the (spanned) cell position of the vertical merge needs to be freed up -->
<! -- The following vertical merge three cells (in the last tab of this line), so the last two td tabs of the next two lines should not be written ~, otherwise the same will overflow Oh ~ -->
<td>4th row 1st</td><td>4th row 2nd</td><td rowspan="3">Vertically merged three cells</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>5th row 1st</td><td>5th row 2nd</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>6th row 1st</td><td>6th row 2nd</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</body>
</html>
colspan
ブラウザでレンダリングすると(ブラウザでhtmlファイルを開くと)こんな感じになります~。

上記の要約は
rowspan
のセルを水平方向にマージしている。
html
垂直方向のセル結合を実現する〜。
さて、これで
case
2つの属性値(つまり、マージされた行数またはマージされた列数)は、この2つのパラメータをsqlで生成し、それをフロントエンドの学生に提供して使用させるために必要なものです。これは浅い意味ですが、では深い意味は何でしょうか?
/この2つのパラメータをsqlで生成し、それをフロントエンドの学生に提供することがまず必要です。
- セルの水平方向の結合の場合
を使用する必要があります。
when
+
then
+
sql
この節では水平方向のマージが必要かどうかを判断していると考えるのが妥当であり(水平方向のマージの値を与えることが重要)、そうすることで起こりうるトラブルとしては
aggregation
もちろん最終手段として)冗長になりますが、もちろんこのセクションでは水平マージのセルについては話しません
- 垂直方向のセル結合の場合
ステップ1
.???? を使用する場合
Window function
+
rowspan
を使用して、マージする必要があるカラムの数を同じだけ計算するため、生成された
step1
同じ列の場合、値は同じになります(下図参照)。
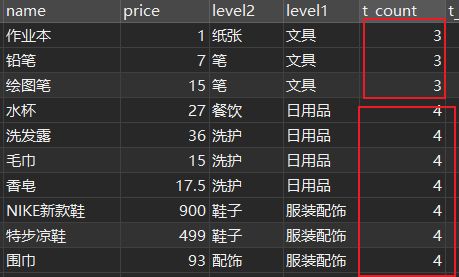
ステップ2
. ???? .... を渡すことができますので
backwards sequence
を使用して、ウィンドウ内の値の合計を生成することも可能である。
order by
列、ハハ? は、マージされた数値の1列目です。.ビンゴ
ウィンドウのカラムは逆順にソートされています
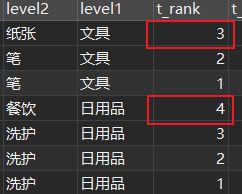
合計列数+反転列数
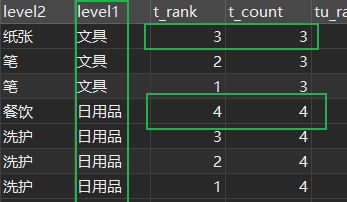
ステップ3
.???? 1 つのデータ列のマージを行うことができるので、2 つの列のマージも行うことができます (これは副列にもなり得ます、注意してください。
drop table if EXISTS report2 ;
CREATE TABLE report2 (
"id" varchar(10) primary key,
"name" varchar(50),
"price" numeric,
"level2" varchar(50) ,
"level1" varchar(50)
);
(マージされた行の影響ああ)、ここで単にマージされた値の列の生成を包装の層の後にそれぞれ、ああ、次の図の緑の部分に注意してください?
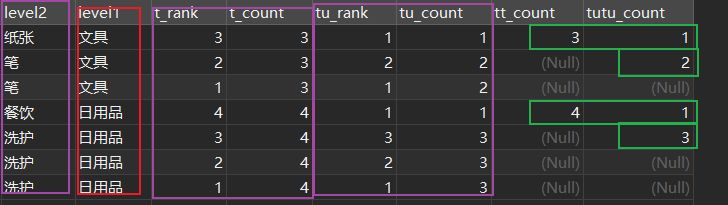
テストスクリプトで試してみてください。~
2.2 テーブル構造
INSERT INTO "report2"("id", "name", "price", "level2", "level1") VALUES ('0015 ', 'shampoo', '36', 'care', 'daily use');
INSERT INTO "report2"("id", "name", "price", "level2", "level1") VALUES ('0008 ', 'soap', '17.5', 'toiletries', 'daily necessities');
INSERT INTO "report2"("id", "name", "price", "level2", "level1") VALUES ('0007 ', 'fries', '7.5', 'junk food', 'snacks');
INSERT INTO "report2"("id", "name", "price", "level2", "level1") VALUES ('0009 ', 'instant noodles', '3.5', 'junk food', 'snacks');
INSERT INTO "report2"("id", "name", "price", "level2", "level1") VALUES ('0004 ', 'spicy sticks', '5.6', 'junk food', 'snacks');
INSERT INTO "report2"("id", "name", "price", "level2", "level1") VALUES ('0006 ', 'iPhone X', '9600', 'small appliance', 'appliance');
INSERT INTO "report2"("id", "name", "price", "level2", "level1") VALUES ('0003 ', 'watches', '1237.55', 'small appliances', 'appliances');
INSERT INTO "report2"("id", "name", "price", "level2", "level1") VALUES ('0012 ', 'TV', '3299', 'big appliances', 'appliances');
INSERT INTO "report2"("id", "name", "price", "level2", "level1") VALUES ('0016 ', 'washing machine', '4999', 'large appliance', 'appliance');
INSERT INTO "report2"("id", "name", "price", "level2", "level1") VALUES ('0013 ', 'scarves', '93', 'accessories', 'clothing accessories');
INSERT INTO "report2"("id", "name", "price", "level2", "level1") VALUES ('0017 ', 'Tebow Sandals', '499', 'Shoes', 'Clothing Accessories');
INSERT INTO "report2"("id", "name", "price", "level2", "level1") VALUES ('0001 ', 'NIKE new shoes', '900', 'shoes', 'clothing accessories');
INSERT INTO "report2"("id", "name", "price", "level2", "level1") VALUES ('0002 ', 'jacket', '110.9', 'top', 'clothing accessory');
INSERT INTO "report2"("id", "name", "price", "level2", "level1") VALUES ('0014 ', 'workbook', '1', 'paper', 'stationery');
INSERT INTO "report2"("id", "name", "price", "level2", "level1") VALUES ('0005 ', 'pencils', '7', 'pens', 'stationery');
INSERT INTO "report2"("id", "name", "price", "level2", "level1") VALUES ('0010 ', 'mugs', '27', 'catering', 'daily necessities');
INSERT INTO "report2"("id", "name", "price", "level2", "level1") VALUES ('0011 ', 'towels', '15', 'toiletries', 'daily necessities');
INSERT INTO "report2"("id", "name", "price", "level2", "level1") VALUES ('0018 ', 'drawing pen', '15', 'pen', 'stationery');
INSERT INTO "report2"("id", "name", "price", "level2", "level1") VALUES ('0019 ', 'soda', '3.5', 'other', 'snacks');
2.3 テーブルフィールドのコメント
<テーブル フィールド コメント イド 主キー 名前 製品名 価格 価格 レベル2 二次分類 レベル1 第一階層分類2.4 テーブルデータ
select
t1.*,
case when t_rank=t_count then t_count else null end as level1_row,
case when tu_rank=tu_count then tu_count else null end as level2_row
from
(
select
*,
row_number() over (PARTITION by level1 order by level1 asc) t_rank,
count(1) over (PARTITION by level1) t_count,
row_number() over(PARTITION by level1,level2 order by level1,level2 asc) tu_rank,
count(1) over (PARTITION by level1,level2) tu_count
from report2 order by level1
) t1 order by t1.level1,t_rank desc,t_count desc,tu_rank desc,tu_count desc;
3. ???? 結果セット 最終解答
sql
の赤い部分は、フロントエンドの子供たちに必要なマージ値 ? ~
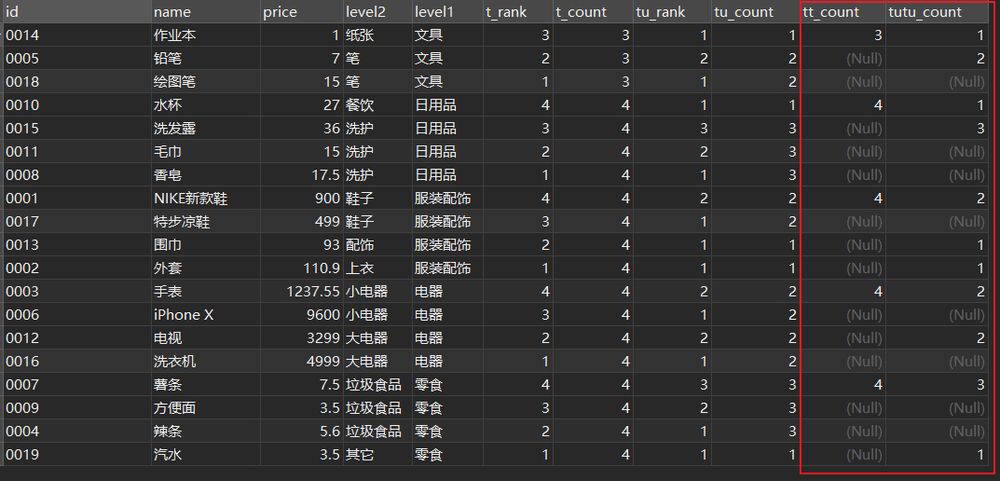
上記の問題を読み、解答することができれば
sql
, またバージョンアップおめでとうございます ?
/{コード
関連
-
postgresql 重複データ削除 ケーススタディ
-
PostgreSQLのテーブルをパーティション分割する3つの方法
-
PostgreSQLでデータの一括インポートのパフォーマンスを向上させるn個の方法を説明します。
-
エクセルテーブルのデータをpostgresqlのデータベースにインポートする方法
-
pgAdmin for postgreSQLでサーバーのデータをバックアップする方法
-
PostgreSQLはバッチ実行のためにSQLをファイルに実装しています。
-
Postgresqlのセルフインクリメントidをキーにした場合の重複問題の解決
-
oracle_fdwを介してOracleデータにアクセスするためのPostgreSQLの手順
-
postgresqlのjsonbデータの問い合わせと変更方法
-
PostgreSQLで時間指定タスクを実装する4つの方法
最新
-
nginxです。[emerg] 0.0.0.0:80 への bind() に失敗しました (98: アドレスは既に使用中です)
-
htmlページでギリシャ文字を使うには
-
ピュアhtml+cssでの要素読み込み効果
-
純粋なhtml + cssで五輪を実現するサンプルコード
-
ナビゲーションバー・ドロップダウンメニューのHTML+CSSサンプルコード
-
タイピング効果を実現するピュアhtml+css
-
htmlの選択ボックスのプレースホルダー作成に関する質問
-
html css3 伸縮しない 画像表示効果
-
トップナビゲーションバーメニュー作成用HTML+CSS
-
html+css 実装 サイバーパンク風ボタン
おすすめ
-
PostgreSQLのURL解決方法
-
Centos環境でのPostgresqlのインストールと設定、環境変数の設定Tips
-
Postgresqlの行から列への高度な応用と要約のアイデア
-
PostgreSQLでバッファキャッシュにデータを読み込む方法
-
Postgresql データベース timescaledb timescaledb 問題 大容量データテーブルをスーパーテーブルに変換すること
-
Postgresqlのデータベース権限まとめ
-
GROUP BY句での定数使用に関するPostgreSQLの特別な制限について説明します。
-
PostgreSQLがバキュームテーブルの情報を収集する必要があることを発見する方法
-
Postgresqlのデータは、2つのフィールドを追加し、一意の操作を統合する
-
PostgreSQLにおけるsequence、serial、identityの使い方の違いについて