React-NativeにおけるイベントリスナーDeviceEventEmitter
基本的な構文
react-nativeでのイベントリスニングは、DeviceEventEmitterというプラグインを使って行います。ここでは、基本的な構文について、以下のように説明します。
1. リスナーの設定
リスナーを受け取りたい場所に、one.jsのページの場合、リスナーを追加する
import { DeviceEventEmitter } from 'react-native';
...
componentDidMount() {
//Receive a listener
this.listener = DeviceEventEmitter.addListener('notification name', (message) => {
//what you want to do when you receive the listener
console.log(message); //Listen
})
}
componentWillUnmount() {
//Remove the listener
if (this.listener) {
this.listener.remove();
}
}
...
上記のコードから、リスナーはDeviceEventEmitterを介して設定され、React-Nativeのライフサイクルに沿って、コンポーネントがロードされたときにリスニングし、コンポーネントがアンロードされたときにリスナーを削除していることがわかります
2. リスナーのトリガー
one.jsのページでリスナーをトリガーする必要がある場合、別のページでペナルティを課すことができます。トリガーするページを2.jsと仮定すると、コードは次のようになります。
import { DeviceEventEmitter } from 'react-native';
...
startEmit() {
//prepare the value and send the listener
const message = 'listen';
DeviceEventEmitter.emit('notification name', message);
}
...
インスタンス操作
ここでは、グローバルリスニングイベントを検証するために2つのページを使用して、ここでは"react-navigation"("1.5.12")、ジャンプインタフェース、まず我々は最初のインターフェイスを実装するために行く、このインタフェースではリスナーを設定するには、コードを次に示すように使用されています。
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Button, Text, View, DeviceEventEmitter } from 'react-native';
class One extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { result: 'I am the default' }
}
componentDidMount() {
// Receive a listener
this.listener = DeviceEventEmitter.addListener('changeResult', (message) => {
// What you want to do when you receive a listener // Listening
this.setState({ result: message });
});
}
componentWillUnmount() {
// Remove the listener
if (this.listener) { this.listener.remove(); }
}
_onChange = () => {
const { navigation } = this.props;
navigation.navigate('Two');
};
render() {
return (
<View style={{ flex: 1, justifyContent: 'center', alignItems: 'center' }}>
<Button onPress={this._onChange} title="Jump to second page" />
<Text style={{ fontSize: 20, marginTop: 30 }}>{this.state.result}</Text>
</View>
);
}
}
export default One;
その後、2番目のインターフェースを完成させます。ここでは、1番目のインターフェースをリッスンしているイベントのトリガーを次のコードで実行します。
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Button, View, DeviceEventEmitter } from 'react-native';
class Two extends Component {
startEmit = () => {
// Prepare the value, send the listener
const message = 'The listener was sent through to allow the value of the one page to be changed';
DeviceEventEmitter.exit('changeResult', message);
};
render() {
return (
<View style={{ flex: 1, justifyContent: 'center', alignItems: 'center' }}>
<Button onPress={this.startEmit} title="Triggers the first page's listener event" />
</View>
);
}
}
export default Two;
では、どのように見えるか見てみましょう。
<センター [エミット]
[エミット]
ソースコードの説明
基本的な使い方ができたので、one.jsのページでクリック(command+左クリック)してソースコードの情報を見ることができるかどうか調べてみましょう。
DeviceEventEmitter
プラグインを使用すると、次のようなインターフェイス・コードが表示されます。
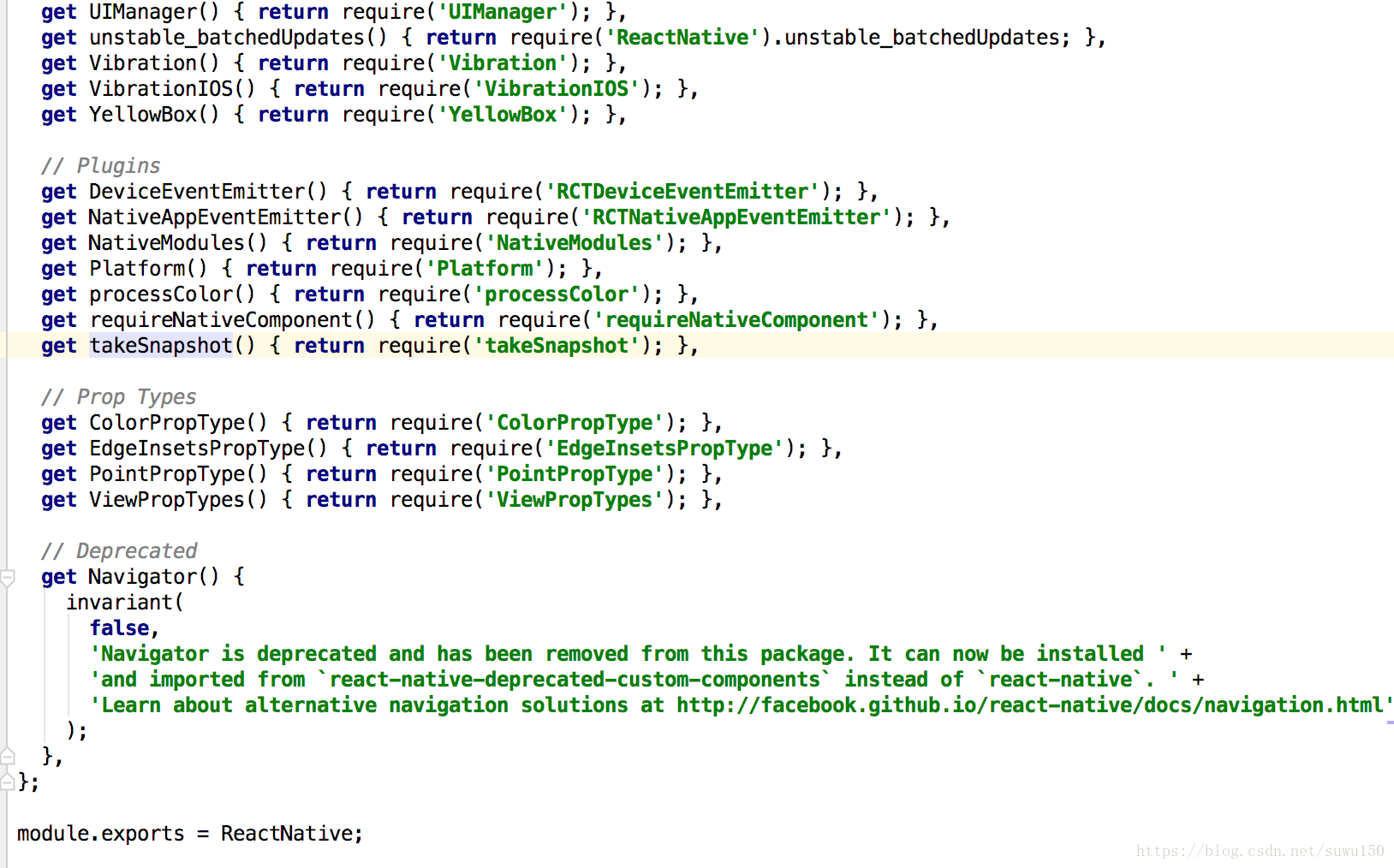 DeviceEventEmitter
DeviceEventEmitter
プラグインでは、次のようなコードがあります。
get DeviceEventEmitter() { return require('RCTDeviceEventEmitter'); },
これはつまり
DeviceEventEmitter
実装の基本はRCTDeviceEventEmitterなので、さらに下を見ると、Libarayフォルダに以下のようなインタフェースがあります。
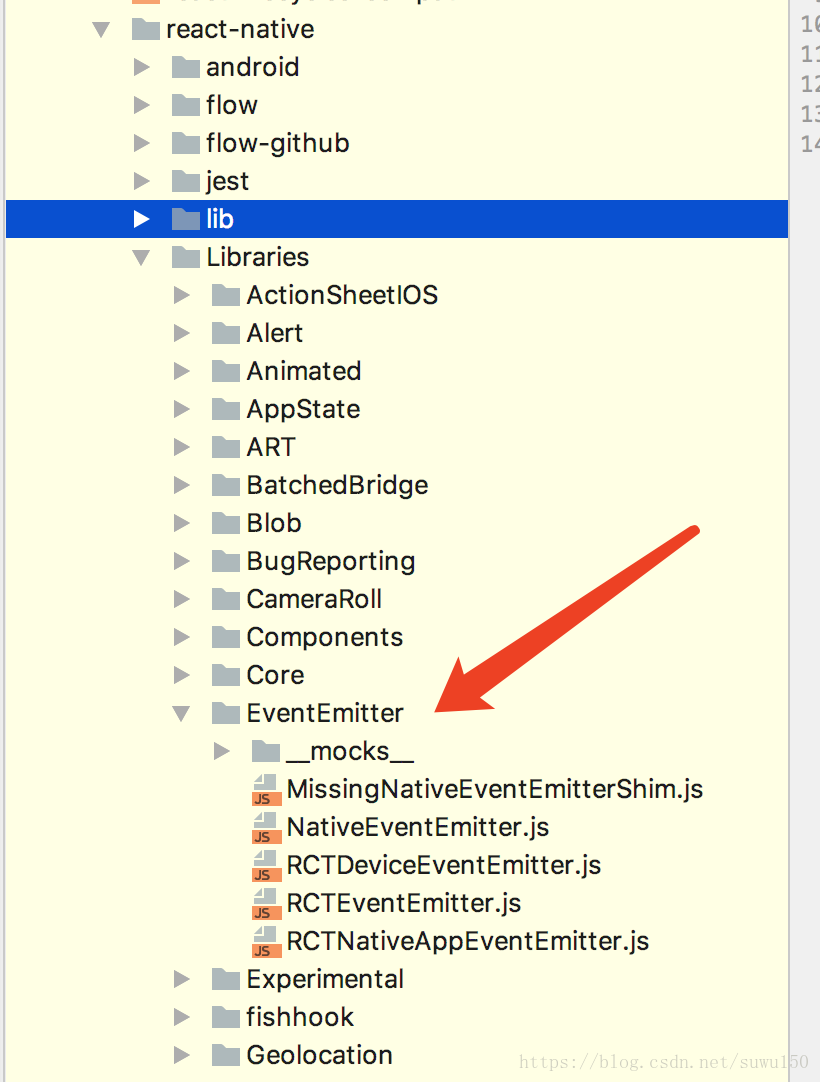 [エミット]
次に、RCTDeviceEventEmitter.js ファイルを探し、そこからコピーした以下のコードを見つけてください。
[エミット]
次に、RCTDeviceEventEmitter.js ファイルを探し、そこからコピーした以下のコードを見つけてください。
/**
* Deprecated - subclass NativeEventEmitter to create granular event modules instead of
* adding all event listeners directly to RCTDeviceEventEmitter.
*/
class RCTDeviceEventEmitter extends EventEmitter {
sharedSubscriber: EventSubscriptionVendor;
constructor() {
const sharedSubscriber = new EventSubscriptionVendor();
super(sharedSubscriber);
this.sharedSubscriber = sharedSubscriber;
}
addListener(eventType: string, listener: Function, context: ?Object): EmitterSubscription {
if (__DEV__) {
checkNativeEventModule(eventType);
}
return super.addListener(eventType, listener, context);
}
removeAllListeners(eventType: ?string) {
if (__DEV__) {
checkNativeEventModule(eventType);
}
super.removeAllListeners(eventType);
}
removeSubscription(subscription: EmitterSubscription) {
if (subscription.emitter ! == this) {
subscription.emitter.removeSubscription(subscription);
} else {
super.removeSubscription(subscription);
}
}
}
module.exports = new RCTDeviceEventEmitter();
コードから、実装されているメソッドはaddListenerであることがわかりますが、それ以外に使用しているメソッドがないことがわかります。
const EventEmitter = require('EventEmitter');
const EventSubscriptionVendor = require('EventSubscriptionVendor');
そこで、次のようなインターフェイスを見ることができる。
<センター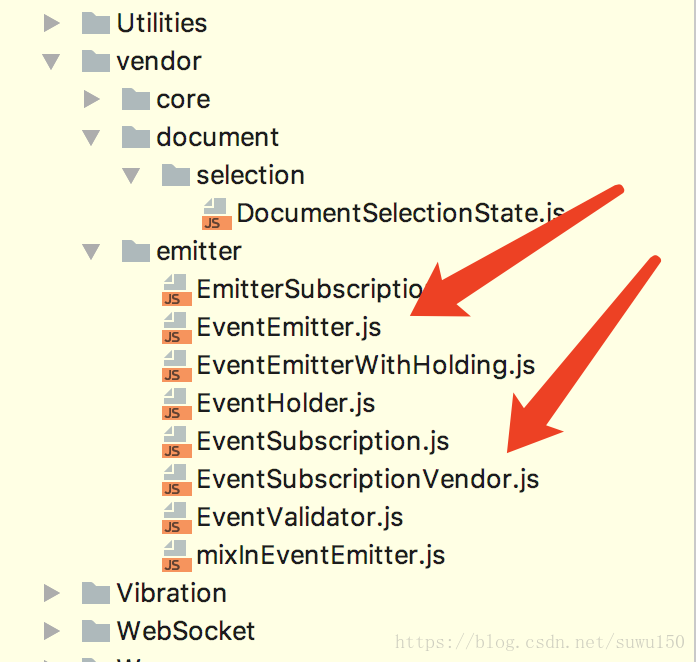
必要なファイルを見るには、EventEmitter.jsファイルを開くと、それを実装したコードが以下のように表示されます。
/**
* Copyright (c) 2015-present, Facebook, Inc.
* This source code is licensed under the MIT license found in the
* This source code is licensed under the MIT license found in the
This source code is licensed under the MIT license found in the * LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree.
*
* @providesModule EventEmitter
* @noflow
* @typecheck
*/
'use strict';
const EmitterSubscription = require('EmitterSubscription');
const EventSubscriptionVendor = require('EventSubscriptionVendor');
const emptyFunction = require('fbjs/lib/emptyFunction');
const invariant = require('fbjs/lib/invariant');
/**
* @class EventEmitter
* @description
* An EventEmitter is responsible for managing a set of listeners and publishing
* In addition to the
In addition to the * data for the given event it also sends a event control object which allows
In addition to the * data for the given event it also sends an event control object which allows * the listeners/handlers to prevent the default behavior of the given event.
*The emitter is designed to prevent the default behavior of the given event.
* The emitter is designed to be generic enough to support all the different
* The emitter is designed to be generic enough to support all the different contexts in which one might want to emit events.
It is a simple multicast * mechanism on top of which extra functionality can be composed.
For example, a * more advanced emitter may use an EventHolder and EventFactory.
*/For example, a * more advanced emitter may use an EventHolder and EventFactory.
class EventEmitter {
_subscriber: EventSubscriptionVendor;
_currentSubscription: ?EmitterSubscription;
/* ***
* @constructor
*
* @param {EventSubscriptionVendor} subscriber - Optional subscriber instance
* If omitted, a new subscriber will be created for the emitter.
*/
constructor(subscriber: ?EventSubscriptionVendor) {
this._subscriber = subscriber || new EventSubscriptionVendor();
}
/**
Adds a listener to be invoked when events of the specified type are * emitted.
* An optional calling context may be provided.
* An optional calling context may be provided.
The data arguments * emitted will be passed to the listener function.
* TODO: Annotate the listener arg's type.
This is tricky because listeners * can be invoked with varargs.
This is tricky because listeners * can be invoked with varargs.
* @param {string} eventType - Name of the event to listen to.
* @param {function} listener - Function to invoke when the specified event is
* emitted
* @param {*} context - Optional context object to use when invoking the
* listener
*/
addListener(
eventType: string, listener: Function, context: ?Object): EmitterSubscription {
return (this._subscriber.addSubscription(
eventType,
new EmitterSubscription(this, this._subscriber, listener, context)
) : any);
}
/**
* Similar to addListener, except that the listener is removed after it is
This is the same as addListener, except that the listener is removed after it is * invoked once.
* @param {string}
* @param {string} eventType - Name of the event to listen to
* @param {function} listener - Function to invoke only once when the
function to invoke only once when the * specified event is emitted
* @param {*} context - Optional context object to use when invoking the
* listener
*/
once(eventType: string, listener: Function, context: ?Object): EmitterSubscription {
return this.addListener(eventType, (.. .args) => {
this.removeCurrentListener();
listener.apply(context, args);
});
}
/**
* Removes all of the registered listeners, including those registered as
* listener maps.
* @param {?string}
* @param {?string} eventType - Optional name of the event whose registered
*
* Provides an API that can be called during an eventing cycle to remove the
* This allows a developer to provide an event
* object that can remove the listener (or listener map) during the
* invocation.
If it is called when not inside the * invocation.
* If it is called when not inside of an emitting cycle it will throw.
* If it is called when not inside of an emitting cycle it will throw.
* @throws {Error} When called not during an eventing cycle
* @example
* @example
* var subscription = emitter.addListenerMap({
* someEvent: function(data, event) {
* console.log(data);
* emitter.removeCurrentListener();
* }
* });
*
* emitter.exit('someEvent', 'abc'); // logs 'abc'
* emitter.emit('someEvent', 'def'); // does not log anything
*/
removeCurrentListener() {
invariant(
! !this._currentSubscription,
'Not in an emitting cycle; there is no current subscription'
);
this.removeSubscription(this._currentSubscription);
}
/* * Removes a specific subscription.
* Called by the `remove()` method of the
Called by the `remove()` method of the * subscription itself to ensure any necessary cleanup is performed.
*/Called by the `remove()` method of the * subscription itself to ensure any necessary cleanup is performed.
removeSubscription(subscription: EmitterSubscription) {
invariant(
subscription.emitter === this,
'Subscription does not belong to this emitter.'
);
this._subscriber.removeSubscription(subscription);
}
/**
* Returns an array of listeners that are currently registered for the given
* event.
*
* @param {string} eventType - Name of the event to query
* @returns {array}
*/
listeners(eventType: string): [EmitterSubscription] {
const subscriptions: ? [EmitterSubscription] = (this._subscriber.getSubscriptionsForType(eventType): any);
return subscriptions
? subscriptions.filter(emptyFunction.thatReturnsTrue).map(
function(subscription) {
return subscription.listener;
})
: [];
}
/* Emits an event of the given type with the given data.
* Emits an event of the given type with the given data.
All handlers of that * particular type will be notified.
All handlers of that * particular type will be notified.
* @param {string} eventType - Name of the event to emit
* @param {... *} Arbitrary arguments to be passed to each registered listener
* @example
* @example
* emitter.addListener('someEvent', function(message) {
* console.log(message);
* });
*
* emitter.emit('someEvent', 'abc'); // logs 'abc'
*/
emit(eventType: string) {
const subscriptions: ? [EmitterSubscription] = (this._subscriber.getSubscriptionsForType(eventType): any);
if (subscriptions) {
for (let i = 0, l = subscriptions.length; i < l; i++) {
const subscription = subscriptions[i];
// The subscription may have been removed during this event loop.
if (subscription) {
this._currentSubscription = subscription;
subscription.listener.apply(
subscription.context,
Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 1)
);
}
}
this._currentSubscription = null;
}
}
/**
* Removes the given listener for event of specific type.
* @param {string} eventType - Name of the event to emit.
* @param {string} eventType - Name of the event to emit
* @param {function} listener - Function to invoke when the specified event is
* emitted
* @example
* @example
* emitter.removeListener('someEvent', function(message) {
* console.log(message);
* }); // removes the listener if already registered
*
*/
removeListener(eventType: String, listener) {
const subscriptions: ? [EmitterSubscription] = (this._subscriber.getSubscriptionsForType(eventType): any);
if (subscriptions) {
for (le
上記のコードの中で、one.jsやtwo.jsで使っているメソッド、例えば、string型のイベントタイプ、リスニングに使うメソッド、コンテキストを渡すことでサブスクリプションを追加するaddListenerは、以下のように見つけることができました。
addListener(
eventType: string, listener: Function, context: ?Object): EmitterSubscription {
return (this._subscriber.addSubscription(
eventType,
new EmitterSubscription(this, this._subscriber, listener, context)
) : any);
}
また、次のコードに示すように、イベントタイプ別にサブスクライブされたすべてのイベントを反復して、指定された eventType に対するサブスクリプションの詳細を取得し、そのパラメータを apply メソッド経由でコンテキストに渡す exit メソッドもあります。
emit(eventType: string) {
const subscriptions: ? [EmitterSubscription] = (this._subscriber.getSubscriptionsForType(eventType): any);
if (subscriptions) {
for (let i = 0, l = subscriptions.length; i < l; i++) {
const subscription = subscriptions[i];
// The subscription may have been removed during this event loop.
if (subscription) {
this._currentSubscription = subscription;
subscription.listener.apply(
subscription.context,
Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 1)
);
}
}
this._currentSubscription = null;
}
}
これが、リクエストを開始したときのメッセージの処理方法です。もちろん、その過程でイベントを処理するコードが他にもいくつかありますので、ここではそのすべてを説明しませんが
DeviceEventEmitterはこうして使われる
最新
-
nginxです。[emerg] 0.0.0.0:80 への bind() に失敗しました (98: アドレスは既に使用中です)
-
htmlページでギリシャ文字を使うには
-
ピュアhtml+cssでの要素読み込み効果
-
純粋なhtml + cssで五輪を実現するサンプルコード
-
ナビゲーションバー・ドロップダウンメニューのHTML+CSSサンプルコード
-
タイピング効果を実現するピュアhtml+css
-
htmlの選択ボックスのプレースホルダー作成に関する質問
-
html css3 伸縮しない 画像表示効果
-
トップナビゲーションバーメニュー作成用HTML+CSS
-
html+css 実装 サイバーパンク風ボタン
おすすめ
-
ハートビート・エフェクトのためのHTML+CSS
-
HTML ホテル フォームによるフィルタリング
-
HTML+cssのボックスモデル例(円、半円など)「border-radius」使いやすい
-
HTMLテーブルのテーブル分割とマージ(colspan, rowspan)
-
ランダム・ネームドロッパーを実装するためのhtmlサンプルコード
-
Html階層型ボックスシャドウ効果サンプルコード
-
QQの一時的なダイアログボックスをポップアップし、友人を追加せずにオンラインで話す効果を達成する方法
-
sublime / vscodeショートカットHTMLコード生成の実装
-
HTMLページを縮小した後にスクロールバーを表示するサンプルコード
-
html のリストボックス、テキストフィールド、ファイルフィールドのコード例