Kubernetesジョブコントローラーのソースコード解析
2022-02-25 17:10:04
著者:[email protected]、WaltonWang@csdn
<ブロッククオート要約:平均的なユーザーは、学習とジョブを使用して、公式文書で十分ですが、あなたは変態であれば、あなたは常に、ジョブコントローラとPodの管理でデプロイメントコントローラ、RestartPolicyと他の違いに加えて、何が違うのか疑問に思うでしょうか。実際には、最近KubernetesのプロジェクトでTensorFlowに従事しているため、ジョブマッピングにしたいTensorFlowワーカータスクを分散、トレーニングデータの目的を達成するために、リソースリソースの自動回復を。このブログの記事は、ジョブコントローラのコードを介して主な内部フローを分析します。
実装フローチャート
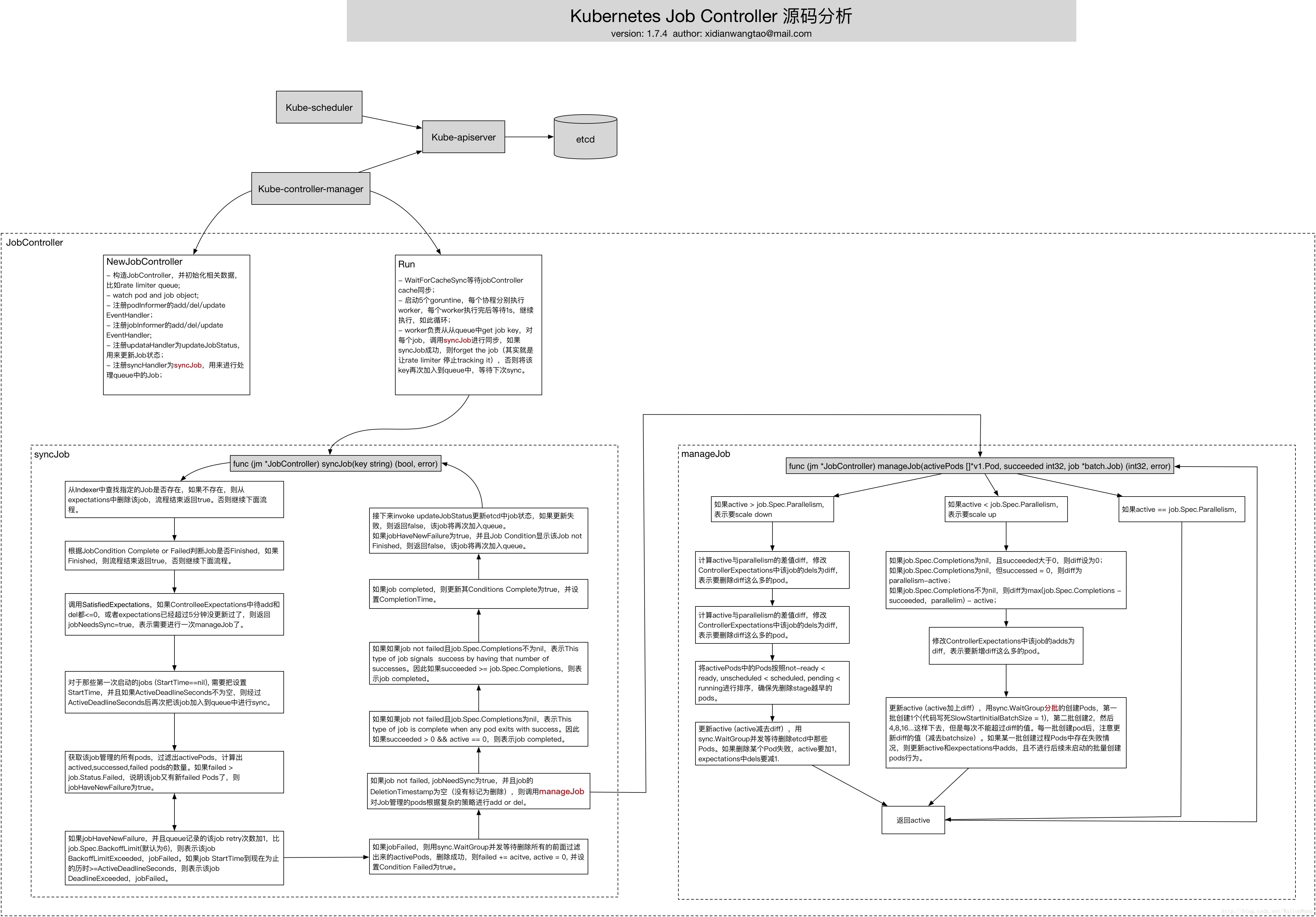
新しいJobController
type JobController struct {
kubeClient clientset.Interface
podControl controller.PodControlInterface
// To allow injection of updateJobStatus for testing.
updateHandler func(job *batch.Job) error
syncHandler func(jobKey string) (bool, error)
// podStoreSynced returns true if the pod store has been synced at least once.
// Added as a member to the struct to allow injection for testing.
podStoreSynced cache.InformerSynced
// jobStoreSynced returns true if the job store has been synced at least once.
// Added as a member to the struct to allow injection for testing.
jobStoreSynced cache.InformerSynced
// A TTLCache of pods creates/deletes each rc expects to see
expectations controller.ControllerExpectationsInterface
// A store of jobs
JobLister batchv1listers.
// A store of pods, populated by the podController
podStore corelisters.PodLister
// Jobs that need to be updated
queue workqueue.RateLimitingInterface
recorder record.EventRecorder
EventRecorder }
func NewJobController(podInformer coreinformers.PodInformer, jobInformer batchinformers.JobInformer, kubeClient clientset.Interface) * JobController {
eventBroadcaster := record.NewBroadcaster()
eventBroadcaster.StartLogging(glog.Infof)
// TODO: remove the wrapper when every clients have moved to use the clientset.
eventBroadcaster.StartRecordingToSink(&v1core.EventSinkImpl{Interface: v1core.New(kubeClient.CoreV1().RESTClient()).Events(& quot;")})
if kubeClient ! = nil && kubeClient.CoreV1().RESTClient().GetRateLimiter() ! = nil {
metrics.RegisterMetricAndTrackRateLimiterUsage("job_controller", kubeClient.CoreV1().RESTClient().GetRateLimiter())
}
jm := &JobController{
kubeClient: kubeClient,
podControl: controller.RealPodControl{
KubeClient: kubeClient,
Recorder: eventBroadcaster.NewRecorder(scheme.Scheme, v1.EventSource{Component: "job-controller"}),
},
expectations: controller.NewControllerExpectations(),
queue: workqueue.NewNamedRateLimitingQueueue(workqueue.NewItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter(DefaultJobBackOff, MaxJobBackOff), " job"),
recorder: eventBroadcaster.NewRecorder(scheme.Scheme, v1.EventSource{Component: "job-controller"}),
}
jobInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: jm.enqueueController,
UpdateFunc: jm.updateJob,
DeleteFunc: jm.enqueueController,
})
jm.jobLister = jobInformer.Lister()
jm.jobStoreSynced = jobInformer.Informer().HasSynced
podInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: jm.addPod,
UpdateFunc: jm.updatePod,
DeleteFunc: jm.deletePod,
})
jm.podStore = podInformer.Lister()
jm.podStoreSynced = podInformer.Informer().HasSynced
jm.updateHandler = jm.updateJobStatus
jm.syncHandler = jm.syncJob
return jm
}
- JobController を構築し、レートリミッターキューなどの関連データを初期化します。
- ウォッチポッドとジョブオブジェクト
- podInformerのadd/del/update EventHandlerを登録します。
- jobInformerのadd/del/update EventHandlerを登録します。
- updataHandlerをupdateJobStatusとして登録し、Jobの状態を更新するために使用する。
- syncHandlerをsyncJobとして登録し、キュー内のジョブを処理するために使用します。
JobControllerの実行
// Run the main goroutine responsible for watching and syncing jobs.
func (jm *JobController) Run(workers int, stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
defer jm.queue.ShutDown()
glog.Infof("Starting job controller")
defer glog.Infof("Shutting down job controller")
if !controller.WaitForCacheSync("job", stopCh, jm.podStoreSynced, jm.jobStoreSynced) {
return
}
for i := 0; i < workers; i++ {
go wait.Until(jm.worker, time.Second, stopCh)
}
<-stopCh
}
// The worker runs a worker thread that just dequeues items, processes them, and marks them done.
// It enforces that the syncHandler is never invoked concurrently with the same key.
func (jm *JobController) worker() {
for jm.processNextWorkItem() {
}
}
func (jm *JobController) processNextWorkItem() bool {
key, quit := jm.queue.
if quit {
return false
Get() if quit { return false }
defer jm.queue.Done(key)
forget, err := jm.syncHandler(key.(string))
if err == nil {
if forget {
jm.queue.Forget(key)
}
return true
}
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("Error syncing job: %v", err))
jm.queue.AddRateLimited(key)
return true
}
// syncJob will sync the job with the given key if it has had its expectations fulfilled, meaning
// it did not expect to see any more of its pods created or deleted.
// concurrently with the same key.
func (jm *JobController) syncJob(key string) (bool, error) {
startTime := time.Now()
defer func() {
glog.V(4).Infof("Finished syncing job %q (%v)", key, time.Now().Sub(startTime))
}()
ns, name, err := cache.SplitMetaNamespaceKey(key)
if err ! = nil {
return false, err
}
if len(ns) == 0 || len(name) == 0 {
return false, fmt.Errorf("invalid job key %q: either namespace or name is missing", key)
}
sharedJob, err := jm.jobLister.Jobs(ns).Get(name)
if err ! = nil {
if errors.IsNotFound(err) {
glog.V(4).Infof("Job has been deleted: %v", key)
jm.expectations.DeleteExpectations(key)
return true, nil
}
return false, err
}
job := *sharedJob
// if job was finished previously, we don't want to redo the termination
if IsJobFinished(&job) {
return true, nil
}
// retrieve the previous number of retry
previousRetry := jm.queue.NumRequeues(key)
// Check the expectations of the job before counting active pods, otherwise a new pod can sneak in
// and update the expectations after we've retrieved active pods from the store.
// the store after we've checked the expectation, the job sync is just deferred till the next relist.
jobNeedsSync := jm.expectations.SatisfiedExpectations(key)
pods, err := jm.getPodsForJob(&job)
if err ! = nil {
return false, err
}
activePods := controller.FilterActivePods(pods)
active := int32(len(activePods))
succeeded, failed := getStatus(pods)
conditions := len(job.Status.Conditions)
// job first start
Status.StartTime == nil { if job.
Now := metav1.
Job.Status.StartTime = &now
// enqueue a sync to check if job past ActiveDeadlineSeconds
if job.Spec.ActiveDeadlineSeconds ! = nil {
glog.V(4).Infof("Job %s have ActiveDeadlineSeconds will sync after %d seconds",
key, *job.Spec.ActiveDeadlineSeconds)
jm.queue.AddAfter(key, time.Duration(*job.Spec.ActiveDeadlineSeconds)*time.Second)
}
}
var manageJobErr error
jobFailed := false
var failureReason string
var failureMessage string
jobHaveNewFailure := failed > job.Status.Failed
// check if the number of failed jobs increased since the last syncJob
if jobHaveNewFailure && (int32(previousRetry)+1 > *job.Spec.BackoffLimit) {
jobFailed = true
failureReason = "BackoffLimitExceeded"
failureMessage = "Job has reached the specified backoff limit"
} else if pastActiveDeadline(&job) {
jobFailed = true
failureReason = "DeadlineExceeded"
failureMessage = "Job was active longer than specified deadline"
}
if jobFailed {
errCh := make(chan error, active)
jm.deleteJobPods(&job, activePods, errCh)
select {
case manageJobErr = <-errCh:
if manageJobErr ! = nil {
break
}
default:
}
// update status values accordingly
failed += active
active = 0
Status.Conditions = append(job.Status.Conditions, newCondition(batch.JobFailed, failureReason, failureMessage))
jm.record.Event(&job, v1.EventTypeWarning, failureReason, failureMessage)
} else {
if jobNeedsSync && job.DeletionTimestamp == nil {
active, manageJobErr = jm.manageJob(activePods, succeeded, &job)
}
completions := succeeded
complete := false
If job.Spec.Completions == nil {
// This type of job is complete when any pod exits with success.
// Each pod is capable of
// determining whether or not the entire Job is done.
// not expected to fail, but if they do, the failure is ignored.
// pod succeeds, the controller waits for remaining pods to finish, and
// then the job is complete.
if succeeded > 0 && active == 0 {
complete = true
}
} else {
// Job specifies a number of completions. This type of job signals // success by having that number of successes.
// success by having that number of successes.
// start more pods than there are remaining completions, there should
Since we do not // start more pods than there are remaining completions, there should // not be any remaining active pods once this count is reached.
If completions >= *job.Spec.Completions {
complete = true
if active > 0 {
jm.record.Event(&job, v1.EventTypeWarning, "TooManyActivePods", "Too many active pods running after completion count reached")
}
if completions > *job.Spec.Completions {
jm.record.Event(&job, v1.EventTypeWarning, "TooManySucceededPods", "Too many succeeded pods running after completion count reached")
}
}
}
if complete {
Job.Status.Conditions = append(job.Status.Conditions, newCondition(batch.JobComplete, "", ""))
now := metav1.Now()
job.Status.
- WaitForCacheSync jobController のキャッシュが同期するのを待ちます。
- 5 つのゴーランチンを起動し、それぞれがワーカーを個別に同時実行し、各ワーカーの実行後 1 秒待って実行を継続する、といった具合です。
- syncJob が成功したら、そのジョブを忘れ(実際にはレートリミッタがそのジョブを追跡しないようにします)、そうでなければキーを再びキューに追加し、次の同期を待ちます。
シンクジョブ
// manageJob is the core method responsible for managing the number of running
// pods according to what is specified in the job.Spec.
// Does NOT modify
.
func (jm *JobController) manageJob(activePods []*v1.Pod, succeeded int32, job *batch.Job) (int32, error) {
var activeLock sync.Mutex
active := int32(len(activePods))
parallelism := *job.Spec.
jobKey, err := controller.KeyFunc(job)
if err ! = nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("Couldn't get key for job %#v: %v", job, err))
return 0, nil
}
var errCh chan error
if active > parallelism {
diff := active - parallelism
errCh = make(chan error, diff)
jm.expectations.ExpectDeletions(jobKey, int(diff))
glog.V(4).Infof("Too many pods running job %q, need %d, deleting %d", jobKey, parallelism, diff)
// Sort the pods in the order such that not-ready < ready, unscheduled
// < scheduled, and pending < running.
// in the earlier stages whenever possible.
sort.Sort(controller.ActivePods(activePods))
active -= diff
wait := sync.WaitGroup{}
wait.Add(int(diff))
for i := int32(0); i < diff; i++ {
go func(ix int32) {
defer wait.Done()
if err := jm.podControl.DeletePod(job.Namespace, activePods[ix].Name, job); err ! = nil {
defer utilruntime.HandleError(err)
// Decrement the expected number of deletes because the informer won't observe this deletion
glog.V(2).Infof("Failed to delete %v, decrementing expectations for job %q/%q", activePods[ix].Name, job.Namespace, job.Name)
jm.expectations.DeletionObserved(jobKey)
acti
If job.Spec.Completions == nil {
// Job does not specify a number of completions. therefore, number active
// should be equal to parallelism, unless the job has seen at least
// once success, in which leave whatever is running, running.
if succeeded > 0 {
wantActive = active
} else {
wantActive = parallelism
}
} else {
// Job specifies a specific number of completions. Therefore, number
// active should not ever exceed number of remaining completions.
wantActive = *job.Spec.Completions - succeeded
if wantActive > parallelism {
wantActive = parallelism
parallelism { wantActive = parallelism }
wantActive = *job.}
diff := wantActive - active
if diff < 0 {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("More active than wanted: job %q, want %d, have %d", jobKey, wantActive, active))
diff = 0
}
jm.expectations.ExpectCreations(jobKey, int(diff))
errCh = make(chan error, diff)
glog.V(4).Infof("Too few pods running job %q, need %d, creating %d", jobKey, wantActive, diff)
active += diff
wait := sync.WaitGroup{}
// Batch sizes start at SlowStartInitialBatchSize
// and double with each successful iteration in a kind of "slow start".
// This handles attempts to start large numbers of pods that would
// likely all fail with the same error. For example a project with a
// low quota that attempts to create a large number of pods will be
// prevented from spamming the API service with the pod create requests
// after one of its pods fails. Conveniently, this also prevents the
// event spam that those failures would generate.
for batchSize := int32(integer.IntMin(int(diff), controller.SlowStartInitialBatchSize)); diff > 0; batchSize = integer.Int32Min(2* batchSize, diff) {
errorCount := len(errCh)
wait.Add(int(batchSize))
for i := int32(0); i < batchSize; i++ {
go func() {
defer wait.Done()
CreatePodsWithControllerRef(job.Namespace, &job.Spec.Template, job, metav1.NewControllerRef(job, controllerKind ))
if err ! = nil && errors.IsTimeout(err) {
// Pod is created but its initialization has timed out.
// If the initialization is successful eventually, the
// If the initialization is successful eventually, the // controller will observe the creation via the informer.
// If the initialization fails, or if the pod keeps
// If the initialization fails, or if the pod keeps // uninitialized for a long time, the informer will not
// receive any update, and the controller will create a new
// pod when the expectation expires.
return
}
if err ! = nil {
defer utilruntime.HandleError(err)
// Decrement the expected number of creates because the informer won't observe this pod
glog.V(2).Infof("Failed creation, decrementing expectations for job %q/%q", job.Namespace, job.Name)
jm.expectations.CreationObserved(jobKey)
activeLock.Lock()
active--
activeLock.Unlo
- 指定されたジョブがIndexerに存在するかどうかを調べ、存在しない場合はExpectationsからそのジョブを削除し、処理終了時にtrueを返します。
- JobCondition CompleteまたはFailedに基づいて、ジョブがFinishedであるかどうかを判断します。Finished の場合は true で終了し、そうでない場合は処理を継続します。
- SatisfiedExpectationsを呼び出し、保留中のControlleeExpectationsのaddとdelが<=0の場合、または期待値が5分以上更新されていない場合、jobNeedsSync=trueを返し、manageJobが必要であることを示します。
- 初めて起動したジョブ(StartTime==nil)については、StartTimeを設定し、ActiveDeadlineSecondsが空でない場合は、ActiveDeadlineSeconds後に再度キューにジョブを追加する必要があります。
- ジョブが管理するすべてのポッドを取得し、activePodsをフィルタリングして、activeed, satisfied, failedのポッドの数を計算します。failed > job.Status.Failed の場合、そのジョブには新しい失敗ポッドがあり、jobHaveNewFailure は真です。
- jobHaveNewFailureとqueueにジョブの再試行回数+1がjob.Spec.BackoffLimit(デフォルトは6)より多い場合、ジョブBackoffLimitExceeded、jobFailed。 if job StartTime up to now If job StartTime is >=ActiveDeadlineSeconds, then the job DeadlineExceeded and the jobFailed.If the Job StartTime up to now, and the job StartTime is >=ActiveDeadlineSeconds.
- jobFailedの場合、sync.WaitGroupと同時に待機して、先にフィルタリングしたactivePodをすべて削除し、削除に成功したらfailed += acitve, active = 0、Condition Failedをtrueに設定します。
- ジョブが失敗しておらず、jobNeedSyncがtrueで、ジョブのDeletionTimestampが空(削除のためにマークされていない)ならば、複雑なポリシーに基づいてジョブによって管理されるポッドを追加または削除するために manageJobを呼び出します。
- job.Spec.Completionsがnilの場合、このタイプのジョブは、いずれかのPodが成功で終了したときに完了することを意味します。
- このタイプのジョブが失敗しなかった場合、その数だけ成功のシグナルを出し、job.Spec. Completionsの場合、そのジョブは完了したことになります。
- ジョブが完了した場合、その条件Completeをtrueに更新し、CompletionTimeを設定します。
- 次に、etcd のジョブの状態を更新するために updateJobStatus を呼び出します。もし更新に失敗したら false を返し、ジョブは再びキューに追加されます。もし jobHaveNewFailure が true で、Job Condition がそのジョブが Finished でないことを示していたら false を返し、そのジョブは再びキューに加えられます。
マネージジョブ
.spec.completions
-
active > job.Spec.Parallelismの場合、スケールダウンすることを意味します。
- activeとparallelの差diffを計算し、ControllerExpectationsのこのジョブのdelsをdiffに変更し、diffが多いポッドを削除することを示す。
- activeとparallelismの差分diffを計算し、ControllerExpectationsのこのジョブのdelsをdiffに変更し、diffからこれだけのポッドを削除したいことを示します。
- activePodsのPodをnot-ready < ready, unscheduled < scheduled, pending < runningでソートし、より早い段階のPodが最初に削除されるようにします。
- sync.WaitGroupでactive(activeからdiffを引いたもの)を更新し、etcdでそれらのPodの削除を同時に待機します。Podの削除に失敗した場合、期待値としてactiveに1、delsに1を加算します。
- アクティブを返す
-
active < job.Spec.の場合は並列処理になります。
スケールアップすることを示す。- job.Spec.Completionsがnilでsucceededが0より大きい場合、diffは0に設定されます。job.Spec.Completionsがnilでsucceeded = 0なら、diffはparallelism-activeとなり、job.Spec.Componentsが0なら、diffは0となります。job.Spec.Completionsがnilでない場合、diffはmax(job.Spec.Completions - succeeded, parallelim) - activeとなり、job.Spec.Completionsがnilではない場合、diffはmax(job.Spec.Completions - succeeded, parallelim) - activeになります.
- ControllerExpectationsのこのジョブのdiffへの追加を変更し、これだけの数のポッドがdiffに追加されることを示します。
- アクティブ(アクティブ+diff)を更新し、sync.WaitGroupでPodをバッチで作成し、最初のバッチは1(コードは死んだSlowStartInitialBatchSize = 1を書く)作成、2番目のバッチは2、次に4、8、16・・・と、毎回diff値を超えないように作成します。ポッドの各バッチが作成された後、diffの値が更新されることに注意してください(batchsizeを差し引いた値)。作成プロセスPodのバッチで障害が発生した場合は、アクティブと期待で追加を更新し、未初心者のポッド作成の動作のその後のバッチを実行しないでください。
- active == job.Spec.Parallelismの場合、activeを返します。
要約
Jobの仕組みや設定方法については、直接以下をお読みください。
公式ドキュメントジョブの完了までの実行
また、ジョブ設定に関する情報もあります。
.spec.parallelism
,
spec.activeDeadlineSeconds
,
spec.activeDeadlineSeconds
このブログ記事は、これらの使い方の説明では、実際に内部でどのように動作しているのかが明確になっていないため、これらを明らかにすることを目的としています。
関連
-
[解決済み] ポッドにバインドされていないPersistentVolumeClaimsがある
-
[解決済み】Kubernetes: kubectl run: コマンドが見つかりません。
-
[解決済み] Kubernetesです。kubectl configからクラスタとコンテキストを削除するにはどうすればいいですか?
-
[解決済み] WaitForFirstConsumer PersistentVolumeClaim バインドする前に最初のコンシューマが作成されるのを待つ。
-
[解決済み] KubernetesのジョブにおけるbackoffLimitの理解
-
[解決済み] no endpoints available for service \"kubernetes-dashboard"
-
[解決済み] kubectlで現在のコンテキストのconfigの詳細を表示するにはどうすればよいですか?
-
[解決済み] kubernetes UnexpectedAdmissionError ロールアウト後。
-
[解決済み] Istio Ingressで "no healthy upstream "が発生する。
-
[解決済み] Kubernetes ReplicaFailure FailedCreate でもイベントなし
最新
-
nginxです。[emerg] 0.0.0.0:80 への bind() に失敗しました (98: アドレスは既に使用中です)
-
htmlページでギリシャ文字を使うには
-
ピュアhtml+cssでの要素読み込み効果
-
純粋なhtml + cssで五輪を実現するサンプルコード
-
ナビゲーションバー・ドロップダウンメニューのHTML+CSSサンプルコード
-
タイピング効果を実現するピュアhtml+css
-
htmlの選択ボックスのプレースホルダー作成に関する質問
-
html css3 伸縮しない 画像表示効果
-
トップナビゲーションバーメニュー作成用HTML+CSS
-
html+css 実装 サイバーパンク風ボタン