ダイアログ(III)--カスタムダイアログビューとパラメータ受け渡し
<スパン この記事がDialogの最後の記事です。最近、仕事がとても忙しかったのですが、暇な時にブログを書きたくなかったのです。疲れていたのでしょう。でも、前に毎月4記事書くという課題を設定したので、無理やりいつも更新していました。馬さんが言っていました。夢を持つことは大切です。万が一、夢が実現した時のために。
関連記事
1.
ダイアログの詳細(I)-基本的な要素の構成
2.
ダイアログ・イン・ディテール(II)-リストの構築について
3.
ダイアログの詳細 (III) - ダイアログビューのカスタマイズとパラメータの受け渡し
今日はカスタムダイアログについてお話します。前の2つの記事は、システムが提供する機能を使ってダイアログを実装していましたが、制限が大きすぎました。独自のビューを定義したい場合、システムの機能は使えないので、ここでカスタムダイアログが必要になります。カスタムダイアログについては、以前の記事 アンドロイドのためのダイアログ関連 うまく書けなかったので、今日は書き直します
<スパン I. 胚の構造
まずはこのビネットの効果からお見せしましょう。
4つのImageViewを横一列に並べたカスタムダイアログボックスです。
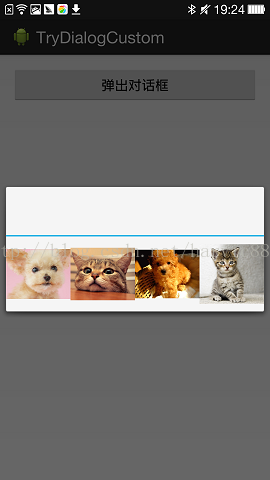
<スパン 1. ダイアログのレイアウト
上記のダイアログスタイルをベースに、ダイアログのレイアウト定義(custom_dialog.xml)を見てみましょう。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"? >
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/log_in_layout"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dip"
android:src="@drawable/animal1"
android:clickable="true"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dip"
android:src="@drawable/animal2"
android:clickable="true"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dip"
android:src="@drawable/animal3"
android:clickable="true"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dip"
android:src="@drawable/animal4"
android:clickable="true"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
</LinearLayout>
<スパン 2. DialogからのDialogクラスの派生
コンストラクターについて。
コンストラクタは3つありますが、ここではそのうちの2つをオーバーライドして使っています。ここで使うのは最初の1つだけで、これはコンテキストを渡すためのものです。
OnCreate()について
OnCreate() で、LayoutInflater を使ってダイアログの View を取得し、 SetContentView を使って CustomDialog クラスのレイアウトとして指定します。
public class CustomDialog extends Dialog {
Context mContext;
public CustomDialog (Context context){
super(context);
mContext = context;
}
public CustomDialog(Context context, int theme) {
super(context, theme);
mContext = context;
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
LayoutInflater inflater = (LayoutInflater) mContext
.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
View layout = inflater.inflate(R.layout.custom_dialog, null);
this.setContentView(layout);
}
}
<スパン 3. メイン機能(MainActivity)
MainActivityでは、ユーザがクリックするとカスタムダイアログボックスのインスタンスをポップアップするButtonを記述しています。
MainActivityのレイアウト。(activity_main.xml)
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_pop_dialog"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="popup_dialog"/>
</RelativeLayout>
コードで処理する。(MainActivity.java)
Btnをクリックすると、CustomDialogクラスのインスタンスが生成され、以下のように表示されます。
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button btn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_pop_dialog);
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
CustomDialog dialog = new CustomDialog(MainActivity.this);
dialog.show();
}
});
}
}
<スパン この部分のソースコードは記事の一番下に記載しています。
<スパン II. ダイアログスタイルの定義
ここで、上にポップアップしたダイアログボックスを振り返ってみましょう。
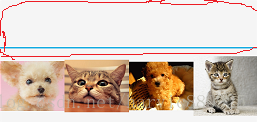
レイアウトでは、4つのImageViewが入った横長のレイアウト、つまりあの4匹の小動物を定義しただけですが、あの一番上の山(赤ペンで丸をつけたもの)はどこから来たのでしょうか?それは削除できるのでしょうか?このセクションでは、スタイルについて説明します。
最初の問題は、ダイアログのスタイルを指定しなかったために、一番上の山だけが存在し、システムはデフォルトのスタイルを使用し、その山はタイトルバーであるということです。
これをなくすには、スタイルをカスタマイズする必要があります。
<スパン 1. カスタムスタイル
私たちのスタイルは、図のように、res/valuesフォルダー内のstyle.xmlファイルに書かれています。style.xmlがない場合は、図のように、自分で新しいものを作ってください。
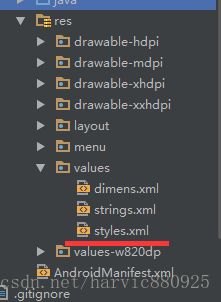
ここで定義されたスタイルコードは次のようになります。
<style name="dialog" parent="android:Theme.Dialog">
<item name="android:windowFrame">@null</item>
<item name="android:windowIsFloating">true</item>
<item name="android:windowContentOverlay">@null</item>
<item name="android:windowNoTitle">true</item>
</style>
まずはパラメータの説明から。
android:windowFrame: 対応するインターフェースの前景画像。
android:windowIsFloating: 画面上で浮いていることを意味します。ここで使用すると、レイアウト全体が画面の中央に配置され、画面上で浮いているのと同じ状態になるので、これはダイアログにのみ適用されます。
android:windowContentOverlay: タイトルバーの影の部分を画像や色で表現する。
android:windowNoTitle: タイトルバーを隠すかどうか、これは上に表示されているタイトルバーです。
スタイルについては雑多なものが多いので、以下の記事を参考にしてください。 AndriodにおけるStyle/Themeの原理とActivityインターフェースファイルの選択プロセス スタイルとテーマの内容については、機会があればまとめて紹介したいと思いますが、今回の記事の焦点ではないので、詳しくは書きません。
<スパン 2. スタイルの使用
<スパン 方法1.
ここでスタイルを使用する方法は2つあり、主にコンストラクタを使用します。ダイアログ用の2つのコンストラクタについて上記で述べたことを思い出してください。
public class CustomDialog extends Dialog {
Context mContext;
public CustomDialog(Context context) {
super(context);
mContext = context;
}
public CustomDialog(Context context, int theme) {
super(context, theme);
mContext = context;
}
............
}
2つ目はテーマのスタイルです。スタイルを使用する最初の方法は、構築時にスタイルを直接渡すことです。この方法で使用する場合、ダイアログボックスを構築すると、次のように表示されます。
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button btn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_pop_dialog);
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
CustomDialog dialog = new CustomDialog(MainActivity.this,R.style.dialog);
dialog.show();
}
});
}
}
つまり、CustomDialogのインスタンスを新規に作成する際に、第2パラメータに上記で定義したスタイルが渡されます。
<スパン
方法2
2つ目の方法は、構築時にスタイルを誰にも渡さず、Contextだけで、内部ではSuper(context,theme)を使ってスタイルを指定するもので、以下のコードで行います。
public class CustomDialog extends Dialog {
Context mContext;
public CustomDialog(Context context) {
super(context,R.style.dialog);
mContext = context;
}
............
}
これは通常、コードをラップして、他の人が外部からスタイルを変更できないようにするときに使用します。
いずれの方法でも、ダイアログのスタイルが指定され、次のようになります。

ほら、上のタイトルバーがなくなった。そして、ここでパラメータ渡しの問題をもう一つ見てみましょう。
<スパン III. パラメータ受け渡し
ここでは、パッシング・インとパッシング・アウトという2つの問題が絡んでいる。
受け渡すこと。 下に2つのボタンがあり、ユーザーが最初のボタンをタップするとダイアログに"From btn 1"と表示され、ユーザーが2番目のボタンをタップするとダイアログに"From btn 2"と表示されます。
パスアウトする。 4つの画像はすべてクリッカブルで、ユーザーがどれかをクリックしたら、そのIDを渡して、MainActivityに設定します。
ここでは分かりやすくするためにダイアログのレイアウトを変更し、横型から縦型に変更しました。そして、MainActiviyの下にImageViewを追加しています。
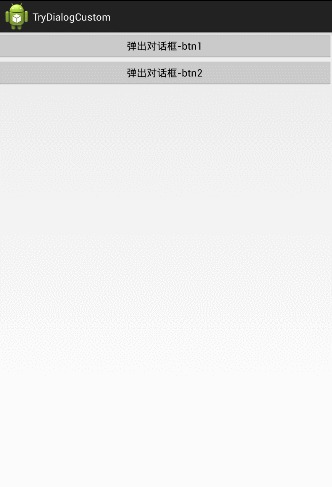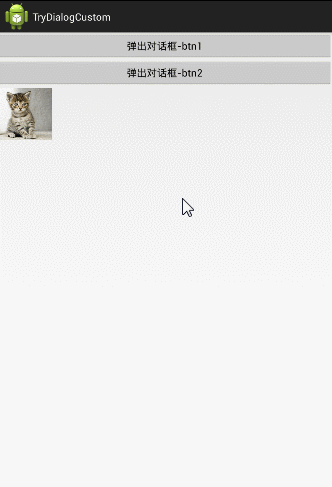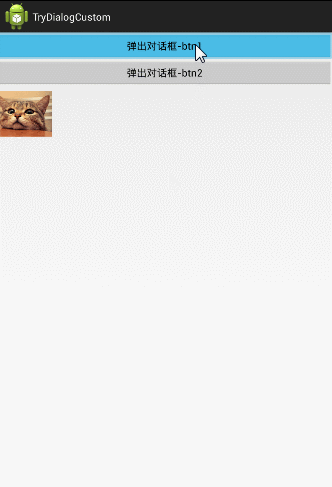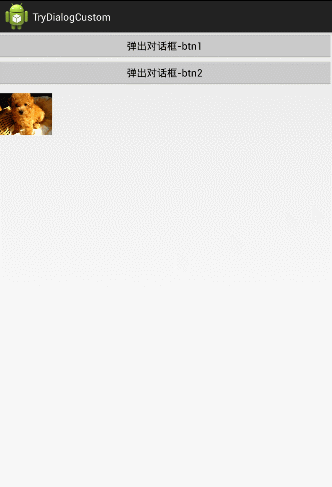
<スパン 1.パスイン
ダイアログにパラメータを渡すには、一般にコンストラクタを使用します。これは単純で、つまり、ダイアログのコンストラクタに自分たちで渡したいパラメータを追加します。ここでは、どのBTNからかを示すために、追加の文字列を渡す必要があります。
ですから、ダイアログのコンストラクタは次のようになります。
public class CustomDialog extends Dialog{
private Context mContext;
private String mStr;
public CustomDialog(Context context, String str, int theme) {
super(context, theme);
mContext = context;
mStr = str;
}
............
}
使用時も、シンプルに。
Button btn2 = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_pop_dialog_2);
btn2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
CustomDialog dialog = new CustomDialog(MainActivity.this,"From btn 2",R.style.dialog);
dialog.show();
}
});
コンストラクタで直接参照を渡すだけ
<スパン 2, パスアウト
コンストラクタを使ってパラメータを渡す方法は知っていますが、ユーザーのアクションに関する情報を渡すのはそれほど簡単ではないので、ここではコールバックを使ってそれを行うことにします
コールバック関数は、以下の手順で使用します。
ダイアログボックスで
public class CustomDialog extends Dialog {
// Use the interface to construct a callback function
public interface ICustomDialogEventListener {
public void customDialogEvent(int valueYouWantToSendBackToTheActivity);
}
private ICustomDialogEventListener onCustomDialogEventListener;
// In the constructor, set in the callback function
public CustomDialog(Context context,
ICustomDialogEventListener onCustomDialogEventListener) {
super(context);
this.onCustomDialogEventListener = onCustomDialogEventListener;
}
// When you want to pass the value back, call the callback function to set the value in
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
Button btnOk = (Button) findViewById(R.id.customDialogButton);
btnOk.setOnClickListener( new Button.OnClickListener()
{
public void onClick(View v) {
onCustomDialogEventListener.customDialogEvent(valueYouWantToSendBackToTheActivity);
dismiss();
}
});
}
}
ダイアログボックスを構成するとき。
final CustomDialog dialog = new CustomDialog(this, new ICustomDialogEventListener() {
public void customDialogEvent(int value) {
// Here we get the value passed back from the dialog
}
});
これが一般的な使い方の流れですが、ここではコールバック関数を用いて、上記のような効果を得る方法を紹介します。
まず、ダイアログに新しいコールバック関数(インターフェース)を作成し、ダイアログのコンストラクタでコールバック関数を渡します。
public class CustomDialog extends Dialog implements View.
//add a callback function to receive the return value from outside
public interface ICustomDialogEventListener {
public void customDialogEvent(int id);
}
private ICustomDialogEventListener mCustomDialogEventListener;
private Context mContext;
private String mStr;
// pass the callback function in
public CustomDialog(Context context, String str, ICustomDialogEventListener listener, int theme) {
super(context, theme);
mContext = context;
mStr = str;
mCustomDialogEventListener = listener;
}
............
}
次に、OnCreate()関数でImageViewのクリックイベントを設定します。クリックイベントを統一的に処理するために、View.OnClickListenerインタフェースをCustomDialogクラスで継承します。
private void bindImageClickEvent(View layout){
ImageView img1 = (ImageView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_image1);
ImageView img2 = (ImageView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_image2);
ImageView img3 = (ImageView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_image3);
ImageView img4 = (ImageView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_image4);
img1.setOnClickListener(this);
img2.setOnClickListener(this);
img3.setOnClickListener(this);
img4.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
LayoutInflater inflater = (LayoutInflater) mContext
.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
View layout = inflater.inflate(R.layout.custom_dialog, null);
TextView tv = (TextView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_text);
tv.setText(mStr);
bindImageClickEvent(layout);//bind ImageView click event
this.setContentView(layout);
}
OnCreate() では、まずダイアログの TextView に渡された String を設定し、次に各 ImageView のクリックイベントをバインドします。
そして、OnClickでの処理です。
主に以下のコードで、ユーザーが現在クリックしているImageViewのIDを元に、このImageViewで使用している画像のDrawableIDをMainActivityに返します。
public void onClick(View view) {
int id = view.getId();
int drawableID = -1;
switch (id){
case R.id.dialog_image1:
drawableID = R.drawable.animal1;
break;
case R.id.dialog_image2:
drawableID = R.drawable.animal2;
break;
case R.id.dialog_image3:
drawableID = R.drawable.animal3;
break;
case R.id.dialog_image4:
drawableID = R.drawable.animal4;
break;
}
if (drawableID ! = -1) {
mCustomDialogEventListener.customDialogEvent(drawableID);
}
dismiss();
}
これでダイアログの構築処理は完了し、完全なダイアログコードは次のようになります。
public class CustomDialog extends Dialog implements View.
//add a callback function to receive the return value from outside
public interface ICustomDialogEventListener {
public void customDialogEvent(int id);
}
private ICustomDialogEventListener mCustomDialogEventListener;
private Context mContext;
private String mStr;
public CustomDialog(Context context) {
super(context);
mContext = context;
}
public CustomDialog(Context context, String str,ICustomDialogEventListener listener,int theme) {
super(context, theme);
mContext = context;
mStr = str;
mCustomDialogEventListener = listener;
}
private void bindImageClickEvent(View layout){
ImageView img1 = (ImageView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_image1);
ImageView img2 = (ImageView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_image2);
ImageView img3 = (ImageView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_image3);
ImageView img4 = (ImageView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_image4);
img1.setOnClickListener(this);
img2.setOnClickListener(this);
img3.setOnClickListener(this);
img4.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
LayoutInflater inflater = (LayoutInflater) mContext
.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
View layout = inflater.inflate(R.layout.custom_dialog, null);
TextView tv = (TextView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_text);
tv.setText(mStr);
bindImageClickEvent(layout);
this.setContentView(layout);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
int id = view.getId();
int drawableID = -1;
switch (id){
case R.id.dialog_image1:
drawableID = R.drawable.animal1;
break;
case R.id.dialog_image2:
drawableID = R.drawable.animal2;
break;
case R.id.dialog_image3:
drawableID = R.drawable.animal3;
break;
case R.id.dialog_image4:
drawableID = R.drawable.animal4;
break;
}
if (drawableID ! = -1) {
mCustomDialogEventListener.customDialogEvent(drawableID);
}
dismiss();
}
}
以下は、ダイアログの構成です。
MainAcitivityで、ボタンがクリックされたら、ICustomDialogEventListenerのインスタンスをnewして、渡された値を受け取ります。
Button btn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_pop_dialog_1);
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
CustomDialog dialog = new CustomDialog(MainActivity.this,"From btn 1",new CustomDialog.ICustomDialogEventListener() {
@Override
public void customDialogEvent(int id) {
ImageView imageView = (ImageView)findViewById(R.id.main_image);
imageView.setImageDrawable(getResources().getDrawable(id));
}
},R.style.dialog);
dialog.show();
}
});
渡されたDrawableIDを受け取ると、それをgcのメインページImageVIewに表示するように設定し、上記の機能は完了です。
さて、今回はここまでです。ダイアログについては基本的に終了し、一般的にはカスタマイズに多くの時間を費やしますので、ここではもう少し詳しく説明します。
ソースコードは2つのパートに分かれています。
1. "TryDialogRudiment": 最初の部分、プロトタイプビルドに対応するコードです。
2, "TryDialogParameter": 2番目と3番目の部分、コード・アンサンブル
<スパン この記事がお役に立ったなら、忘れずにフォローしてくださいね。
ソースコードのアドレスです。
http://download.csdn.net/detail/harvic880925/8370545
原作者の著作権を尊重し、以下のように複製元を明記してください。
http://blog.csdn.net/harvic880925/article/details/42712777
ありがとうございました
<スパン 私の記事がお好きな方は、私の公開サイトがもっと好きになるかもしれません。

最新
-
nginxです。[emerg] 0.0.0.0:80 への bind() に失敗しました (98: アドレスは既に使用中です)
-
htmlページでギリシャ文字を使うには
-
ピュアhtml+cssでの要素読み込み効果
-
純粋なhtml + cssで五輪を実現するサンプルコード
-
ナビゲーションバー・ドロップダウンメニューのHTML+CSSサンプルコード
-
タイピング効果を実現するピュアhtml+css
-
htmlの選択ボックスのプレースホルダー作成に関する質問
-
html css3 伸縮しない 画像表示効果
-
トップナビゲーションバーメニュー作成用HTML+CSS
-
html+css 実装 サイバーパンク風ボタン
おすすめ
-
ハートビート・エフェクトのためのHTML+CSS
-
HTML ホテル フォームによるフィルタリング
-
HTML+cssのボックスモデル例(円、半円など)「border-radius」使いやすい
-
HTMLテーブルのテーブル分割とマージ(colspan, rowspan)
-
ランダム・ネームドロッパーを実装するためのhtmlサンプルコード
-
Html階層型ボックスシャドウ効果サンプルコード
-
QQの一時的なダイアログボックスをポップアップし、友人を追加せずにオンラインで話す効果を達成する方法
-
sublime / vscodeショートカットHTMLコード生成の実装
-
HTMLページを縮小した後にスクロールバーを表示するサンプルコード
-
html のリストボックス、テキストフィールド、ファイルフィールドのコード例