C++-コラムフィッティングフィットシリンダー
著者 スティーブン・ザイ ティエンバオ
著作権について 著作権は著者に帰属します。商業的な複製は著者に、非商業的な複製は出典を明記してください。
シナリオの要件
主要な領域での画像処理では、しばしば面をフィットさせる必要があり、最も多いのは斜めの面ですが、面、球、円柱にもフィットさせることができ、この記事では円柱のフィットについて説明します。
柱面フィッティングの式
![]()
この式に基づいて、カラム表面解析で一般的な評価パラメータであるC3はpowerx、C4はpoweryという、フィットさせる表面の係数を求めることができます。
サーフェスをフィッティングする上で、とてもとても重要な注意点が、xとyの値です。フィールド内では、まずxとyを正規化する必要があります。matlabのmeshgridのような、xとyのデータのグリッドを作成する。例えば、1000*1000の画像で、xのデータの最初の行はすべて-1、最後の行はすべて1で、その間に等しい間隔の増分があり、yのデータの最初の列はすべて-1、最後の列はすべて1、その間に同じ等しい間隔の増分があります。これにより、ZYGOのフィッティング手法など、光学業界の標準と一致する係数値が得られます。
さっそくですが、具体的な実装関数とテストコードです。
機能コード
// Fit the column surface
cv::Mat FitCylinder(const cv::Mat&phase)
{
cv::Mat cyc = ImageCropping(phase);
cv::Mat mask = cv::Mat::zeros(cyc.size(), CV_8UC1);
mask.setTo(255, cyc == cyc);
cv::Mat x, y, ang, mag;
UnitCart(cyc.cols, cyc.rows, x, y);
UnitPolar(x, y, mag, ang);
int samplingInterval = 1;
vector<cv::Point> points;
cv::findNonZero(mask, points);
int pointnumber = static_cast<int>(points.size());
samplingInterval = Max(samplingInterval, static_cast<int>(sqrt(pointnumber) / 100));
// Sampling to improve the speed of computation,
cv::Mat sampling_roi = GridSampling(mask.size(), samplingInterval, samplingInterval);
sampling_roi.setTo(0, ~mask);
// Get the coordinates of the sampling point
std::vector<cv::Point> samplingidx_roi;
cv::findNonZero(sampling_roi, samplingidx_roi);
int len_sam = (int)samplingidx_roi.size();
cv::Mat ang_sampling(len_sam, 1, CV_32FC1, 0.0f);
cv::Mat mag_sampling(len_sam, 1, CV_32FC1, 0.0f);
auto tmpSam = samplingidx_roi.begin();
for (int i = 0; i < len_sam; ++i, ++tmpSam) {
int x = tmpSam-> x;
int y = tmpSam-> y;
ang_sampling.ptr<float>(i)[0] = ang.ptr<float>(y)[x];
mag_sampling.ptr<float>(i)[0] = mag.ptr<float>(y)[x];
}
cv::Mat phase_roi = get<float>(cyc, samplingidx_roi);
cv::Mat dst(len_sam, 6, CV_32FC1, 0.0f);
cv::Mat pow1 = mag_sampling;
cv::Mat X = pow1.mul(cosf(ang_sampling));
cv::Mat Y = pow1.mul(sinf(ang_sampling));
cv::Mat X2 = pow(X, 2.0);
cv::Mat Y2 = pow(Y, 2.0);
cv::Mat XY = X.mul(Y);
for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) {
switch (i) {
case 0: dst.col(i).setTo(1.0f); break; // 0
case 1: X.copyTo(dst.col(i)); break; // 1
case 2: Y.copyTo(dst.col(i)); break; // 2
case 3: X2.copyTo(dst.col(i)); break; // 3
case 4: Y2.copyTo(dst.col(i)); break; // 4
case 5: XY.copyTo(dst.col(i)); break; // 5
default: break;
}
}
cv::Mat result;
cv::solve(dst, phase_roi, result, cv::DECOMP_NORMAL); // Solve equation A'A * dst = dst in A'B,
cv::Mat temp = result.clone();
return result;
}
// Read excel image data
cv::Mat ReadPicFromExcel(string name)
{
cv::Mat result, pic;
ifstream infile(name);
string str;
int col = 0;
while (getline(infile, str))
{
string temp;
stringstream input(str);
col = 0;
while (input >> temp)
{
if (temp == "nan")
{
pic.push_back((nan("")));
}
else {
pic.push_back((atof(temp.c_str())));
}
col++;
}
}
int row = pic.rows / col;
result = pic.reshape(0, row);
infile.close();
return result;
}
// Image cropping
cv::Mat ImageCropping(const cv::Mat &phase) {
// The non-measured area is generally NaN-processed, so the mask drawing only needs to determine if it is a NaN value
cv::Mat mask = cv::Mat::zeros(phase.size(), CV_8UC1);
mask.setTo(255, phase == phase);
int roi_up = 10000;
int roi_down = 0;
int roi_left = 10000;
int roi_right = 0;
int row = phase.rows;
int col = phase.cols;
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
uchar *m = mask.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
if (m[j] ! = 0)
{
if (j < roi_left) roi_left = j;
if (j > roi_right)roi_right = j;
if (i < roi_up)roi_up = i;
if (i > roi_down)roi_down = i;
}
}
}
int w = roi_right - roi_left;
int h = roi_down - roi_up;
// Generally extract the odd size for easy calculation
if (w % 2 == 0)w++;
if (h % 2 == 0)h++;
cv::Mat crop_phase = phase(cv::Rect(roi_left, roi_up, w, h)).clone();
return crop_phase;
}
// meshgrid
void UnitCart(int squaresizex, int squaresizey, cv::Mat& x, cv::Mat& y) {
CV_Assert(squaresizex % 2 == 1);
CV_Assert(squaresizey % 2 == 1);
x.create(squaresizey, squaresizex, CV_32FC1);
y.create(squaresizey, squaresizex, CV_32FC1);
//set the boundary
x.col(0).setTo(-1.0);
x.col(squaresizex - 1).setTo(1.0f);
y.row(0).setTo(1.0);
y.row(squaresizey - 1).setTo(-1.0f);
float deltax = 2.0f / (squaresizex - 1.0f); // the interval between the two elements
float deltay = 2.0f / (squaresizey - 1.0f); // interval of two elements
// Calculate the value of other positions
for (int i = 1; i < squaresizex - 1; ++i) {
x.col(i) = -1.0f + i * deltax;
}
for (int i = 1; i < squaresizey - 1; ++i) {
y.row(i) = 1.0f - i * deltay;
}
}
// polar transformation
void UnitPolar(cv::Mat& x, cv::Mat& y, cv::Mat& mag, cv::Mat& ang) {
//cv::cartToPolar(x, y, mag, ang, indegree); //right-angle coordinates converted to polar coordinates
mag = cv::Mat(x.size(), x.type());
ang = cv::Mat(x.size(), x.type());
int row = mag.rows;
int col = mag.cols;
for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i)
{
float*m = mag.ptr<float>(i);
float*a = ang.ptr<float>(i);
float*xx = x.ptr<float>(i);
float*yy = y.ptr<float>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < col; ++j)
{
m[j] = sqrt(xx[j] * xx[j] + yy[j] * yy[j]);
a[j] = atan2(yy[j], xx[j]);
}
}
}
// Sampling speedup
cv::Mat GridSampling(const cv::Size& size, int rowinterval, int colinterval) {
cv::Mat dst(size, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(0));
// Set the position point for sampling
int Row = dst.rows;
int Col = dst.cols;
for (int row = 0; row < Row; row += rowinterval) {
for (int col = 0; col < Col; col += colinterval) {
dst.at<uchar>(row, col) = 255;
}
}
return dst;
}
// Get the calculated data
template <typename T>
cv::Mat get(const cv::Mat& src,const std::vector<cv::Point>& idx)
{
int num = (int)idx.size();
cv::Mat dst(num, 1, src.type());
/* pragma omp parallel for is a directive in OpenMP that
indicates that the next for loop will be executed by multiple threads, plus there can be no relationship between each loop */
#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) {
dst.at<T>(i, 0) = src.at<T>(idx[i]);
}
return dst;
}
// Image data cos processing
cv::Mat cosf(const cv::Mat& src) {
CV_Assert(src.type() == CV_32FC1);
cv::Mat dst(src.size(), src.type());
int cols = src.cols;
int rows = src.rows;
//returns the bool value to determine if the storage is contiguous.
if (src.isContinuous() && dst.isContinuous())
{
cols *= rows;
rows = 1;
}
// Calculate the cos() of each element
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
const float* srci = src.ptr<float>(i);
float* dsti = dst.ptr<float>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
dsti[j] = std::cosf(srci[j]);
}
}
return dst;
}
// image data sin processing
cv::Mat sinf(const cv::Mat& src) {
CV_Assert(src.type() == CV_32FC1);
cv::Mat dst(src.size(), src.type());
int cols = src.cols;
int rows = src.rows;
//returns the bool value to determine if the storage is contiguous.
if (src.isContinuous() && dst.isContinuous())
{
cols *= rows;
rows = 1;
}
// Calculate sin() for each element
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
const float* srci = src.ptr<float>(i);
float* dsti = dst.ptr<float>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
dsti[j] = std::sinf(srci[j]);
}
}
return dst;
}
// image data squaring
cv::Mat pow(cv::InputArray src, double power) {
cv::Mat dst;
cv::pow(src, power, dst);
return dst;
}
C++テストコード
#include<iostream>
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<ctime>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
#define Max(a, b) a > b ? a : b
cv::Mat FitCylinder(const cv::Mat&phase);
cv::Mat ReadPicFromExcel(string name);
cv::Mat ImageCropping(const cv::Mat &phase);
void UnitCart(int squaresizex, int squaresizey, cv::Mat& x, cv::Mat& y);
void UnitPolar(cv::Mat& x, cv::Mat& y, cv::Mat& mag, cv::Mat& ang);
cv::Mat GridSampling(const cv::Size& size, int rowinterval, int colinterval);
template <typename T>
cv::Mat get(const cv::Mat& src, const std::vector<cv::Point>& idx);
cv::Mat cosf(const cv::Mat& src);
cv::Mat sinf(const cv::Mat& src);
cv::Mat pow(cv::InputArray src, double power);
int main(void)
{
cv::Mat phase = ReadPicFromExcel("test.xls");
cv::Mat coef = FitCylinder(phase);
for (int i = 0; i < coef.rows; ++i)
{
cout << "coef " << i << " : " << coef.at<float>(i, 0) << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
// Fit the column surface
cv::Mat FitCylinder(const cv::Mat&phase)
{
cv::Mat cyc = ImageCropping(phase);
cv::Mat mask = cv::Mat::zeros(cyc.size(), CV_8UC1);
mask.setTo(255, cyc == cyc);
cv::Mat x, y, ang, mag;
UnitCart(cyc.cols, cyc.rows, x, y);
UnitPolar(x, y, mag, ang);
int samplingInterval = 1;
vector<cv::Point> points;
cv::findNonZero(mask, points);
int pointnumber = static_cast<int>(points.size());
samplingInterval = Max(samplingInterval, static_cast<int>(sqrt(pointnumber) / 100));
// Sampling to improve the speed of computation,
cv::Mat sampling_roi = GridSampling(mask.size(), samplingInterval, samplingInterval);
sampling_roi.setTo(0, ~mask);
// Get the coordinates of the sampling point
std::vector<cv::Point> samplingidx_roi;
cv::findNonZero(sampling_roi, samplingidx_roi);
int len_sam = (int)samplingidx_roi.size();
cv::Mat ang_sampling(len_sam, 1, CV_32FC1, 0.0f);
cv::Mat mag_sampling(len_sam, 1, CV_32FC1, 0.0f);
auto tmpSam = samplingidx_roi.begin();
for (int i = 0; i < len_sam; ++i, ++tmpSam) {
int x = tmpSam-> x;
int y = tmpSam-> y;
ang_sampling.ptr<float>(i)[0] = ang.ptr<float>(y)[x];
mag_sampling.ptr<float>(i)[0] = mag.ptr<float>(y)[x];
}
cv::Mat phase_roi = get<float>(cyc, samplingidx_roi);
cv::Mat dst(len_sam, 6, CV_32FC1, 0.0f);
cv::Mat pow1 = mag_sampling;
cv::Mat X = pow1.mul(cosf(ang_sampling));
cv::Mat Y = pow1.mul(sinf(ang_sampling));
cv::Mat X2 = pow(X, 2.0);
cv::Mat Y2 = pow(Y, 2.0);
cv::Mat XY = X.mul(Y);
for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) {
switch (i) {
case 0: dst.col(i).setTo(1.0f); break; // 0
case 1: X.copyTo(dst.col(i)); break; // 1
case 2: Y.copyTo(dst.col(i)); break; // 2
case 3: X2.copyTo(dst.col(i)); break; // 3
case 4: Y2.copyTo(dst.col(i)); break; // 4
case 5: XY.copyTo(dst.col(i)); break; // 5
default: break;
}
}
cv::Mat result;
cv::solve(dst, phase_roi, result, cv::DECOMP_NORMAL); // Solve equation A'A * dst = dst in A'B,
cv::Mat temp = result.clone();
return result;
}
// Read excel image data
cv::Mat ReadPicFromExcel(string name)
{
cv::Mat result, pic;
ifstream infile(name);
string str;
int col = 0;
while (getline(infile, str))
{
string temp;
stringstream input(str);
col = 0;
while (input >> temp)
{
if (temp == "nan")
{
pic.push_back((nan("")));
}
else {
pic.push_back((atof(temp.c_str())));
}
col++;
}
}
i
if (j < roi_left) roi_left = j;
if (j > roi_right)roi_right = j;
if (i < roi_up)roi_up = i;
if (i > roi_down)roi_down = i;
}
}
}
int w = roi_right - roi_left;
int h = roi_down - roi_up;
// Generally extract the odd size for easy calculation
if (w % 2 == 0)w++;
if (h % 2 == 0)h++;
cv::Mat crop_phase = phase(cv::Rect(roi_left, roi_up, w, h)).clone();
return crop_phase;
}
// meshgrid
void UnitCart(int squaresizex, int squaresizey, cv::Mat& x, cv::Mat& y) {
CV_Assert(squaresizex % 2 == 1);
CV_Assert(squaresizey % 2 == 1);
x.create(squaresizey, squaresizex, CV_32FC1);
y.create(squaresizey, squaresizex, CV_32FC1);
//set the boundary
x.col(0).setTo(-1.0);
x.col(squaresizex - 1).setTo(1.0f);
y.row(0).setTo(1.0);
y.row(squaresizey - 1).setTo(-1.0f);
float deltax = 2.0f / (squaresizex - 1.0f); // the interval between the two elements
float deltay = 2.0f / (squaresizey - 1.0f); // interval of two elements
// Calculate the value of other positions
for (int i = 1; i < squaresizex - 1; ++i) {
x.col(i) = -1.0f + i * deltax;
}
for (int i = 1; i < squaresizey - 1; ++i) {
y.row(i) = 1.0f - i * deltay;
}
}
// polar transformation
void UnitPolar(cv::Mat& x, cv::Mat& y, cv::Mat& mag, cv::Mat& ang) {
//cv::cartToPolar(x, y, mag, ang, indegree); //right-angle coordinates converted to polar coordinates
mag = cv::Mat(x.size(), x.type());
ang = cv::Mat(x.size(), x.type());
int row = mag.rows;
int col = mag.cols;
for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i)
{
float*m = mag.ptr<float>(i);
float*a = ang.ptr<float>(i);
float*xx = x.ptr<float>(i);
float*yy = y.ptr<float>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < col; ++j)
{
m[j] = sqrt(xx[j] * xx[j] + yy[j] * yy[j]);
a[j] = atan2(yy[j], xx[j]);
}
}
}
// Sampling speedup
cv::Mat GridSampling(const cv::Size& size, int rowinterval, int colinterval) {
cv::Mat dst(size, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(0));
// Set the position point for sampling
int Row = dst.rows;
int Col = dst.cols;
for (int row = 0; row < Row; row += rowinterval) {
for (int col = 0; col < Col; col += colinterval) {
dst.at<uchar>(row, col) = 255;
}
}
return dst;
}
// Get the calculated data
template <typename T>
cv::Mat get(const cv::Mat& src,const std::vector<cv::Point>& idx)
{
int num = (int)idx.size();
cv::Mat dst(num, 1, src.type());
/* pragma omp parallel for is a directive in OpenMP that
indicates that the next for loop will be executed by multiple threads, plus there can be no relationship between each loop */
#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) {
dst.at<T>(i, 0) = src.at<T>(idx[i]);
}
return dst;
}
// Image data cos processing
cv::Mat cosf(const cv::Mat& src) {
CV_Assert(src.type() == CV_32FC1);
cv::Mat dst(src.size(), src.type());
int cols = src.cols;
int rows = src.rows;
//returns the bool value to determine if the storage is contiguous.
if (src.isContinuous() && dst.isContinuous())
{
cols *= rows;
rows = 1;
}
// Calculate the cos() of each element
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
const float* srci = src.ptr<float>(i);
float* dsti = dst.ptr<float>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
dsti[j] = std::cosf(srci[j]);
}
}
return dst;
}
// image data sin processing
cv::Mat sinf(const cv::Mat& src) {
CV_Assert(src.type() == CV_32FC1);
cv::Mat dst(src.size(), src.type());
int cols = src.cols;
int rows = src.rows;
//returns the bool value to determine if the storage is contiguous.
if (src.isContinuous() && dst.isContinuous())
{
cols *= rows;
rows = 1;
}
// Calculate sin() for each element
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
const float* srci = src.ptr<float>(i);
float* dsti = dst.ptr<float>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
dsti[j] = std::sinf(srci[j]);
}
}
return dst;
}
// image data squaring
cv::Mat pow(cv::InputArray src, double power) {
cv::Mat dst;
cv::pow(src, power, dst);
return dst;
}
テスト結果

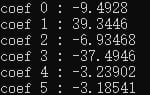

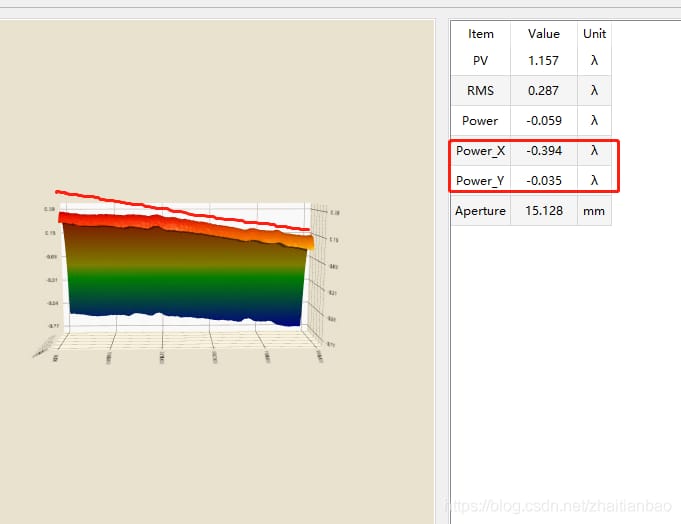
テストケースでは、干渉計の結果が一般的に非常に低いので、値を100倍して、得られたグレースケール画像は、図1に示すように、黒と白の違いを明確に見ることができるように、私は、列の表面データをロードし、図4では、傾斜、白い部分は0よりも大きい値の部分であることも見ることができます; 私はVSで傍受した領域と当社のソフトウェアで傍受した領域が正確に同じではないため、Powerxとパワーの値が異なっている。VSで切り取った面積と弊社ソフトで切り取った面積は全く同じではないので、powerxとpoweryの値は異なるが、大きさが同じであれば、誤差はないことになる。図2のように、VSの出力を100で割って比較すると、coef3がpowerx、coef4がpoweryとなる。
もし、この機能を改善できることがあれば、ぜひ指摘してください。一緒に進歩しませんか?
もしこの記事が役に立ったなら、いいね!で教えてくれたらうれしいです~ Go!
関連
-
C++:ソースファイルを開くことができない問題
-
34:5: エラー: 制御が非ボイド関数の終わりに達する可能性がある [-Werror,-Wreturn-type] エラー解析
-
C++ - 文字列クラス超詳細紹介
-
C++プリントベクター
-
c++ experience summary(1):linux c compile with warning: assign makes pointer from integer without cast reason.
-
警告: この関数では 'p' が初期化されていない状態で使用されることがあります。
-
C++プロジェクトのコンパイル時に再定義の多重定義問題を解決する
-
一意でないテーブル/エイリアス
-
抽象クラス型 "my class "のオブジェクトは使用できません 解決方法
-
C++共通ライブラリ関数一覧
最新
-
nginxです。[emerg] 0.0.0.0:80 への bind() に失敗しました (98: アドレスは既に使用中です)
-
htmlページでギリシャ文字を使うには
-
ピュアhtml+cssでの要素読み込み効果
-
純粋なhtml + cssで五輪を実現するサンプルコード
-
ナビゲーションバー・ドロップダウンメニューのHTML+CSSサンプルコード
-
タイピング効果を実現するピュアhtml+css
-
htmlの選択ボックスのプレースホルダー作成に関する質問
-
html css3 伸縮しない 画像表示効果
-
トップナビゲーションバーメニュー作成用HTML+CSS
-
html+css 実装 サイバーパンク風ボタン
おすすめ
-
std::logic_error' のインスタンスを投げた後に呼び出された実行エラー終了 what(): basic_string::_S_const
-
C/C++共通エラーの概要
-
vs2015 はソースファイル stdio.h を見つけることができない 解決策
-
C++ 文字列における c_str(), data(), copy(p,n) 関数の使用法
-
C++: エラー C2228: '.str' の左側にはクラス/構造体/結合が必要
-
文字列がこのスコープで宣言されていない 問題の解決
-
C++ shared_ptr コンパイルエラー 'shared_ptr' がこのスコープで宣言されていない問題を修正しました。
-
std::allocator<char>::~allocator()' への未定義の参照
-
ベクトル添え字が範囲外のコンテナの使用、その他類似のエラー
-
デバッグエラー Assertion Failed 問題について