AJAX&JSON超詳細解説
2022-02-24 08:36:27
本日の内容
1.AJAX(エイジャックス
A.コンセプト
Concepts
ASynchronous JavaScript And XML
JavaScript
と
XML
非同期と同期 : クライアントサイドとサーバーサイドの相互の通信に基づく
* ( <マーク シンクロナイゼーション ) クライアント 必須 は、サーバー側からの応答を待ちます。 待っている間、クライアントは他のことは何もできない .
* ( <マーク 非同期式
) クライアント は必要ありません。 サーバー側からの応答を待ちます。 サーバーがリクエストを処理している間、クライアントは他のアクションを実行することができます。
Ajax
は、アプリケーションで使用される
ページ全体を再読み込みすることなく
を更新するために
<マーク
部分
新しいページを追加することで
バックエンドでサーバと少量のデータ交換を行うだけで
Ajaxは、ウェブページを非同期で更新することを可能にします。
これはつまり
without reloading the entire page
を使って、ページの一部を更新することができます。
従来のWebページ(Ajaxを使用していない)は、コンテンツを更新する必要がある場合、Webページ全体を再読み込みする必要があります。
The main purpose: to improve the user experience
B.実装
1. JSのネイティブ実装
最も基本的な実装
ステップ
1. コア・オブジェクトの作成 (W3Cを見る)
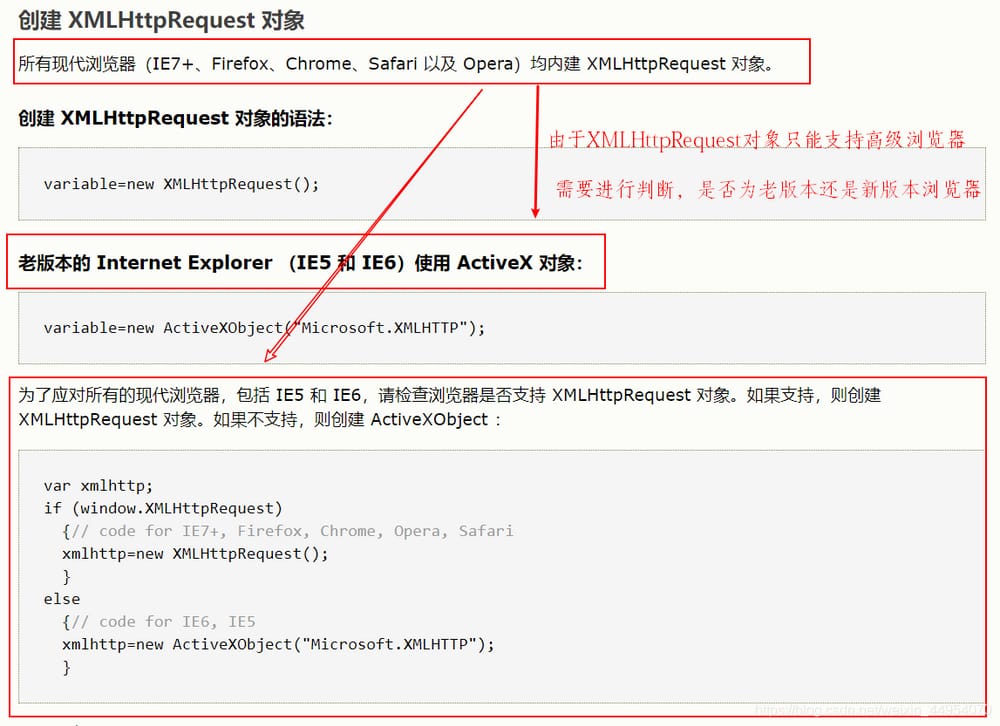
2. 作成したら
to establish a connection
どうやるんだ?
問題を理解するためにW3Cのドキュメントをチェックした
その内訳は
サーバーにリクエストを送信する
その
サーバーの応答を受信し、データを処理する
-
サーバーにリクエストを送信する
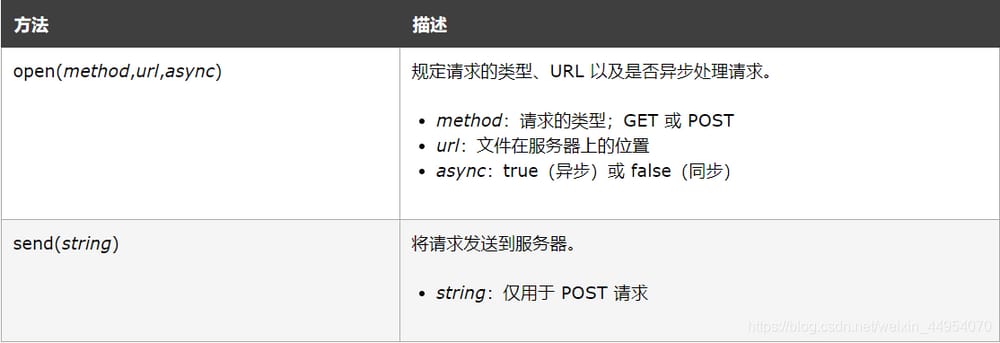
サーバーにリクエストを送信するためにXMLHttpRequestオブジェクトのopen()とsend()メソッドを使用します。
1.1 フォーマット
xmlhttp.open("GET","test1.txt",true); xmlhttp.send();
1.2 パラメーターの説明。
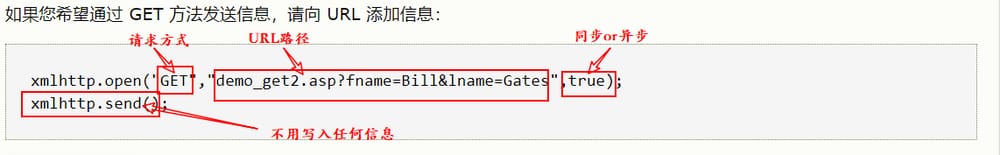
1.3 GETなのかPOSTなのか?
と同じです。
POST
と比較して
GET
は、よりシンプルで高速であり、ほとんどの場合において動作します。
ただし、以下の場合はPOSTリクエストを使用してください。
- キャッシュされたファイルを使用できない(サーバー上のファイルやデータベースを更新するため)
- サーバーに大量のデータを送信する(POSTにはデータ量の制限がない)。
- 未知の文字を含むユーザー入力を送信する場合、GETよりもPOSTの方が安定性と信頼性が高い
The difference between the two
:
依頼者
GET
POST
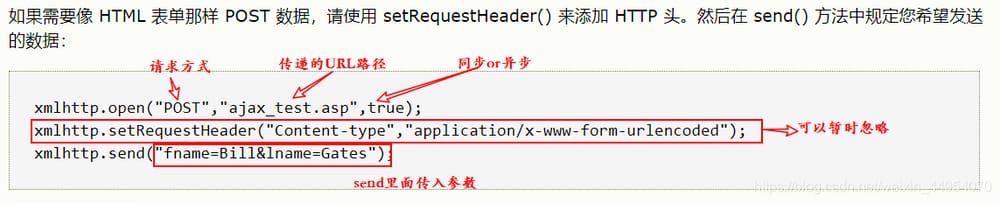
get method
The request parameters are spliced after the URL. send method is a null parameter
post method
The request parameters are defined in the send method
 Receive server response, process data
Get: There are two ways (here only
Receive server response, process data
Get: There are two ways (here only
responseText attribute)
)
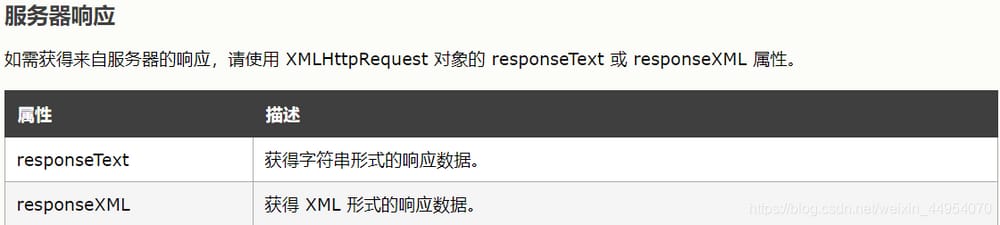
When do we get it?
When the server
responds successfully
and then fetches the
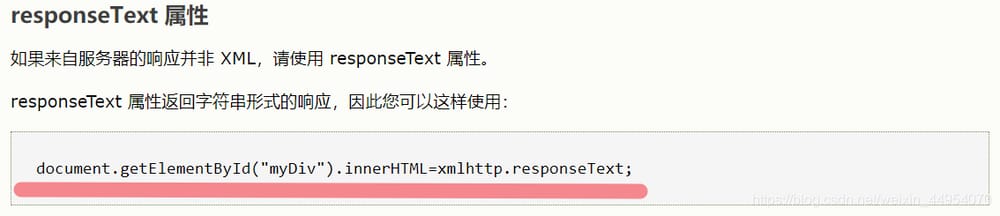
Example
Where the numbers represent
: The
 The overall most primitive JS implementation
The overall most primitive JS implementation
//1. Create the core object
var xmlhttp;
if (window.XMLHttpRequest)
{// code for IE7+, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari
xmlhttp=new XMLHttpRequest();
}
else
{// code for IE6, IE5
xmlhttp=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
<--------------------------------------------------------------------->
// 2. Create the connection
/*
Parameters.
1. request method: GET, POST
* get method, request parameters are spliced after the URL. send method is empty parameter
* post method, request parameters are defined in the send method
2. request URL: 3.
3. synchronous or asynchronous request: true (asynchronous) or false (synchronous)
*/
xmlhttp.open("GET","ajaxServlet?username=tom",true);
<--------------------------------------------------------------------->
//3. Send the request
xmlhttp.send();
<--------------------------------------------------------------------->
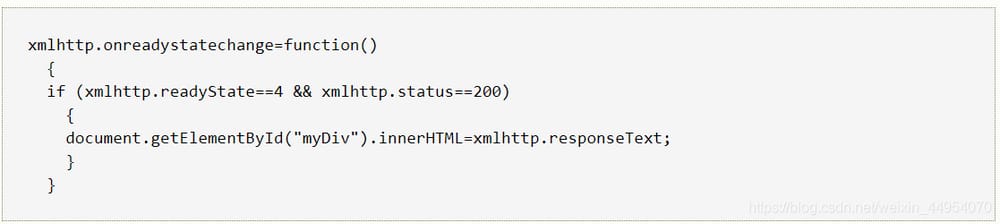
//4. Receive and process the response from the server
//Get: xmlhttp.responseText
//When to get it? When the server response is successful and then get it
//trigger the event onreadystatechange when the readiness state of the xmlhttp object changes.
xmlhttp.onreadystatechange=function()
{
//judge if readyState of readyState is 4, judge if status response status code is 200
if (xmlhttp.readyState==4 && xmlhttp.status==200)
{
//get the server's response result
var responseText = xmlhttp.responseText;
alert(responseText);
}
}
2. JQeury implementation
Why use JQeury for implementation?
The JS implementation is too cumbersome, so we can find another solution
.
Implementation
$.ajax()
* Syntax: $.ajax({key-value pair});
// send an asynchronous request using $.ajax()
$.ajax({
url:"ajaxServlet1111" , // request path
type:"POST" , // request method
//data: "username=jack&age=23", // request parameters
data:{"username":"jack","age":23},
success:function (data) {
alert(data);
},// callback function for successful response
error:function () {
alert("Error... ")
},// callback function that will be executed if there is an error in the request response
dataType:"text"//set the format of the received response data
});
$.get(): sends a get request
* Syntax: $.get(url, [data], [callback], [type])
* Parameters.
* url: request path
* data: request parameter
* callback: callback function
* type: the type of the response result
<--------------------------------------------------------------------->
<script src="js/jquery-3.3.1.min.js"></script>
</head>
<script>
function fun() {
$.get(
//url: request path
url = "/test/jqueryServlet",
//data: request parameters
{"username":"jack"},
//callback: callback function
function (data) {
alert(data)
},
//type: the type of the response result
type="text"
)
}
</script>
<body>
<input type="button" value="click" onclick=fun();>
<input type="text">
</body>
$.post(): send post request
* Syntax: $.post(url, [data], [callback], [type])
* Parameters.
* url: request path
* data: request parameter
* callback: callback function
* type: the type of the response result
<script src="js/jquery-3.3.1.min.js"></script>
</head>
<script>
function fun() {
$.post(
url = "/test/jqueryServlet",
{"username":"jack"},
function (data) {
alert(data)
},
type="text"
)
}
</script>
<body>
<input type="button" value="click" onclick=fun();>
<input type="text">
</body>
2.JSON
A.Concept
Concept.
JavaScript Object Notation JavaScript
Object Notation
Person p = new Person();
p.setName("Zhang San");
p.setAge(23);
p.setGender("Male");
var p = {"name": "Zhang San", "age":23, "gender ": "male"};
Features.
json is now mostly used as a syntax for storing and exchanging text information
Performing the transfer of data
JSON is smaller, faster, and easier to parse than XML.
B.Syntax
1. Basic rules
Data in name/value pairs: json data is made up of key-value pairs
Keys are in quotes
(single and double are fine)
) to cause the
can also be used without quotation marks
Worth taking the value type.
1. number (integer or floating point)
2. strings (
in double quotes)
)
3. Logical values (true or false)
4. arrays (in square brackets) {"persons":[{},{}]}
5. object (in brackets) {"address":{"province": "Shaanxi"...}}
Data separated by commas: multiple key-value pairs separated by commas
Save objects in brackets: use {} to define json format
Square brackets hold arrays: []
What is the key value.
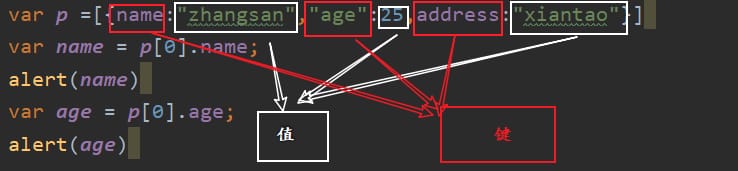
What is an array.
Middle brackets contain curly brackets - >[ {},{} ]
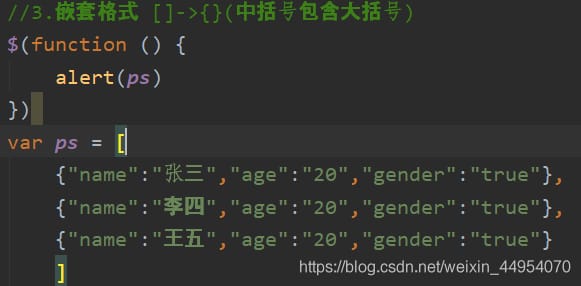
What is the object.
{"object name",[{},{},{}]}
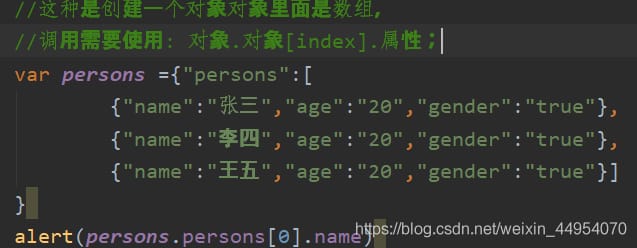 2. Get the data
json object. Key Name
2. Get the data
json object. Key Name
2. json object ["keyname"]
3. array object[index]
4. traversal
//1. Define the basic format
var person = {"name": "Zhang San", age: 23, 'gender': true};
<--------------------------------------------------------------------->
var ps = [{"name": "Zhang San", "age": 23, "gender": true},
{"name": "李四", "age": 24, "gender": true},
{"name": "王五", "age": 25, "gender": false}];
<--------------------------------------------------------------------->
//get all the keys and values in the person object
//for in loop
for(var key in person){
//getting in this way doesn't work. Because the equivalent of person."name"
//alert(key + ":" + person.key);
alert(key + "" + person[key]);
}
<--------------------------------------------------------------------->
//get all values in ps
for (var i = 0; i < ps.length; i++) {
var p = ps[i];
for(var key in p){
alert(key+":"+p[key]);
}
}
C.Interconversion of JSON data and Java objects
JSON parser.
* Common parsers.
Jsonlib
, the
Gson
, fastjson
, jackson
 Create Jackson core object ObjectMapper
Create Jackson core object ObjectMapper
// Create ObjectMapper object
ObjectMapper o = new ObjectMapper();
//automatically escapes the double quotes
String json = "{\"name\":\\"张三\",\"age\":20,\"gander\":\"male\",\"birthday\& quot;:\"2020-04-02\"}";
Call the relevant method of ObjectMapper to perform the conversion
// call readerValue(String,Class
Person person = objectMapper.readValue(json, Person.class);
//print the result, no input after it so it automatically gives a date
//Person{name='Zhang San', age=20, gander='Male', birthday=Thu Apr 02 08:00:00 CST 2020}
System.out.println(person);
2. Java object to JSON conversion
Importing the relevant jar packages for jackson
Create the core Jackson object ObjectMapper
Call the relevant methods of the ObjectMapper to perform the conversion
Conversion methods.
* writeValue(parameter 1, obj):
Parameter 1.
File: Convert the obj object to a JSON string and save it to the specified file
Writer: converts the obj object to a JSON string, and fills the json data into the character output stream
OutputStream: converts the obj object to a JSON string, and fills the json data into the byte output stream
writeValueAsString(obj): convert the object to a json string
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
Person p = new Person("Zhang San", 20, "Male",new Date());
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
String string = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(p);
System.out.println(string);
}
Annotation.
- @JsonIgnore: exclude attribute.
- @JsonFormat: attribute worthy formatting
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd")
private String name;
private int age;
private String gander;
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd")
//@JsonIgnore
private Date birthday;
Complex java object conversions
- List: arrays
@Test
//java List to Json
//list stores objects in the way
public void test3() throws Exception {
Person p = new Person("Zhang San", 20, "Male",new Date());
Person w = new Person("张三", 20, "男",new Date());
Person e = new Person("张三", 20, "男",new Date());
List
2. Map: consistent object format
@Test
//java List to Json
//map's key-value pair approach
public void test4() throws Exception {
Map
Case
Verify that the username exists
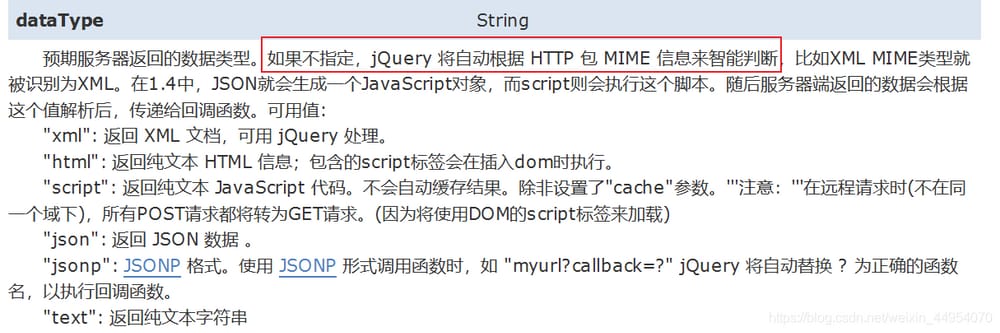
The data from the server response, when used on the client, is to be used as json data format. There are two solutions.
1.
$.get(type)
:Set the last parameter
type
specified as "
json
"
Then on the server side, write
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
2. set on the server side
MIME
Type ()
response.setContentType
("
application/json
;
charset=utf-8
");
Code examples
package com.xiaoge.servlet;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**Map; import java.util.
* Created by Administrator on 2020/4/4 11:10
* @author Administrator
*/
@WebServlet("/findUsernameServlet")
public class FindUsernameServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
<---------------------------------------------------------------------->
//1. Get the username
String username = request.getParameter("username");
<---------------------------------------------------------------------->
//2. Call the service layer to determine if the username exists
// Expect the server to respond back with the following data format: {"userExsit":true,"msg":"This username is too popular, please change one"}
// {"userExsit":false,"msg":"Username available"}
//
//response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
Map
html code block
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Registration page</title>
<script src="js/jquery-3.3.1.min.js"></script>
<---------------------------------------------------------------------->
<script>
//after the page has finished loading
$(function () {
//bind blur event to username
$("#username").blur(function () {
//Get the value of the username text input box
var username = $(this).val();
//Send ajax request
// expect the server to respond back with the following data format: {"userExsit":true,"msg":"This username is too popular, please change one"}
// {"userExsit":false,"msg":"Username available"}
$.get("/test/findUsernameServlet",{username:username},function (data) {
// determine if the value of the userExsit key is true
// alert(data);
var span = $("#s_username");
if(data.userExsit){
//Username exists
span.css("color","red");
span.html(data.msg);
}else{
//username does not exist
span.css("color","green");
span.html(data.msg);
}
});
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<---------------------------------------------------------------------->
<form>
<input type="text" id="username" name="username" placeholder="Please enter username">
<span id="s_username"></span>
<br>
<input type="password" name="password" placeholder="Please enter password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Register"><br>
</form>
</body>
</html>
関連
-
SocketTimeoutExceptionです。読み込みがタイムアウトしました
-
javax.net.ssl.SSLException: 読み取りエラー: ssl=0xdeae5100: システムコール中の I/O エラー、接続 res
-
同期・並行クラスコンテナ
-
アクセス制限です。タイプ 'JPEGCodec' は API エラーではありません。
-
Java - 学生寮管理システム
-
リソースはスタイルシートとして解釈されるが、MIMEタイプはapplication/octet-streamで転送される。
-
Javaデータ型 - StringBuilderとStringBuffer
-
eclipse install plugin thing error: インストールするアイテムの収集中にエラーが発生しました セッションコンテキストは次のとおりです:(profil
-
AxisFault: com.ctc.wstx.exc.WstxEOFException.AxisFault.WstxEOFException: Prolog サービスで予期しない EOF が発生し、接続できません。
-
CloseableHttpResponse
最新
-
nginxです。[emerg] 0.0.0.0:80 への bind() に失敗しました (98: アドレスは既に使用中です)
-
htmlページでギリシャ文字を使うには
-
ピュアhtml+cssでの要素読み込み効果
-
純粋なhtml + cssで五輪を実現するサンプルコード
-
ナビゲーションバー・ドロップダウンメニューのHTML+CSSサンプルコード
-
タイピング効果を実現するピュアhtml+css
-
htmlの選択ボックスのプレースホルダー作成に関する質問
-
html css3 伸縮しない 画像表示効果
-
トップナビゲーションバーメニュー作成用HTML+CSS
-
html+css 実装 サイバーパンク風ボタン
おすすめ
-
スタイルが読み込まれず、ブラウザコンソールでエラーが報告される。リソースはスタイルシートとして解釈されますが、MIMEタイプtext/htmlで転送されます。
-
スキャナは、タイプに解決することはできません最もルーキー初心者の質問
-
SyntaxError: JSON入力の予期せぬ終了 解決策とアイデア
-
java mail 530 5.7.0 Must issue STARTTLS command first エラー解決法
-
Swagger の @ApiModelProperty オブジェクト フィールドが表示されない
-
Java GUI プログラミング 4 --- ラベルコンポーネント JLabel
-
Javaコレクションで一般的なcheckForComodification()メソッドは何をするのですか?modCount と expectedModCount の役割?
-
Javaアルゴリズム競技の入出力トピック
-
java 8 ラムダ式 リスト操作 グループ化、フィルタリング、合計、最多、ソート、重複排除
-
ドルイド新バージョンエラー破棄長い時間なし受信接続を解決する。