パイソンホワイトシステム実践プロジェクト200例(ソースコード付き)、練習が大幅にパイソン(Kunpengプログラミング - Pythonの教育新種)のレベルを向上させることができます。
2022-02-22 10:16:31
1.十から二へ
2. 10から8まで
3 10~16歳
4. 文字列からバイトへ
5.文字列に変換する
6. 10からASCII
7.ASCIIから10へ
8.辞書に変換する
9. 浮動小数点型へ
10. 整数に変換する
11. セットに変換する
12. スライスへ
13. タプルへ
14.フローズンセットに移動
15. 商と余り
16. べき乗と余り
17. 四捨五入
19.ドアナンバー
18 変数が占めるバイト数の表示
20. ソート機能
21. 和算関数
22. 計算式
23. 真か偽か
24. 両方共真実
25. 少なくとも1つは真実である
26. ユーザーの入力を得る
27.使用状況の表示
28. 文字列の書式
29. オブジェクトのハッシュ値を返す
30. ファイルを開く
31. ビューオブジェクトタイプ
32. プロパティを作成する2つの方法
33. 電話の可否
34. 属性の動的削除
35. オブジェクトのプロパティを動的に取得する
36. あるオブジェクトがあるプロパティを持つかどうか
37. isinstance
38. 親子鑑定
39. すべてのオブジェクトのルート
40.オブジェクトの全メソッドをワンクリックで表示可能
41. オブジェクトの列挙
43. 範囲イテレータの作成
44. リバース
45.パック
46.フィルター
47. チェーン比較
48. チェーンオペレーション
49.split スプリット**分割
50.置き換える
1.十から二へ
10進数から2進数に変換する。
>>> bin(10)
'0b1010'
2.十から八まで
10進数から8進数への変換。
>>> oct(9)
'0o11'
3 ten to sixteen
10進数から16進数への変換。
>>> hex(15)
'0xf'
4. 文字列からバイトへの変換
文字列をバイト型に変換する
>>> s = "apple"
>>> bytes(s,encoding='utf-8')
b'apple'
5. 文字列に変換する
文字型、数値型などを文字列型に変換する
>>> i = 100
>>> str(i) '100'
6. 10からASCII
10進整数のASCII文字
<ブロッククオート <ブロッククオートchr(65)
'A'
7. ASCIIから10ASCIIへ
文字に対応する10進数
>>> ord('A')
65
8. 辞書に変換する
データ辞書を作成するいくつかの方法
>>> dict()
{}
>>> dict(a='a',b='b')
{'a': 'a', 'b': 'b'}
>>> dict(zip(['a','b'],[1,2]))
{'a': 1, 'b': 2}
>>> dict([('a',1),('b',2)])
{'a': 1, 'b': 2}
9. 浮動小数点型への変換
整数または数値文字列を浮動小数点数に変換する
>>> float(3)
3.0
浮動小数点に変換できない場合はValueErrorとなります。
>>> float('a')
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "
>>> int('12',16)
18
11. Convert to a collection
Returns a set object, with no duplicate elements allowed in the set.
>>> a = [1,4,2,3,1]
>>> set(a)
{1, 2, 3, 4}
12. Convert to slices
class slice(start, stop[, step]) returns a slice object with the index set specified by range(start, stop, step), making the code more readable.
>>> a = [1,4,2,3,1]
>>> my_slice = slice(0,5,2)
>>> a[my_slice]
[1, 2, 1]
13. Turning tuples
tuple() converts an object to an immutable sequence type
>>> a=[1,3,5]
>>> a.append(7)
>>> a
[1, 3, 5, 7]
#Prohibit a from adding or deleting elements, just convert to a tuple
>>> t=tuple(a)
>>> t
(1, 3, 5, 7)
14. Turning a frozen set
Create an unmodifiable collection.
>>> a = frozenset([1,1,3,2,3])
>>> a # a no pop,append,insert etc
frozenset({1, 2, 3})
15. Quotient and remainder
Take the quotient and remainder, respectively
>>> divmod(10,3)
(3, 1)
16. Powers and remainders
All three arguments to pow are given to indicate power and then remainder.
>>> pow(3, 2, 4)
1
17. Rounding
Rounding, with ndigits representing the number of decimal places to be retained.
>>> round(10.045, 2)
10.04
>>> round(10.046, 2)
10.05
18 Viewing the number of bytes occupied by a variable
>>> import sys
>>> a = {'a':1,'b':2.0}
>>> sys.getsizeof(a) # Number of bytes occupied by the variable
240
19. door number
Return the memory address of the object
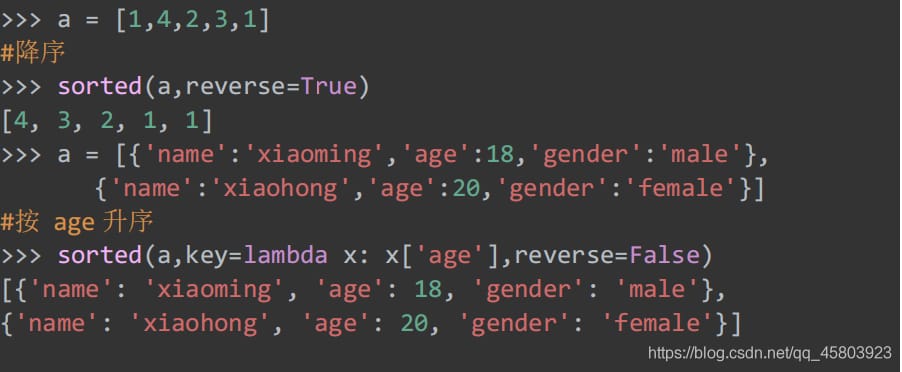
20. Sorting functions
Sorting.
21. Summation functions
Summation.
22. Calculating expressions
Compute the value of a string-type expression
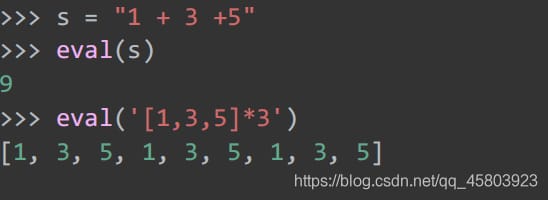
23. True or False

24. All true
Returns True if all elements of the iterable object are true, False otherwise

25. At least one is true
Takes an iterable object and returns True if at least one element of the iterable is true, otherwise it returns False
 26. Get user input
Get user input
26. Get user input
Get user input

27. print Usage
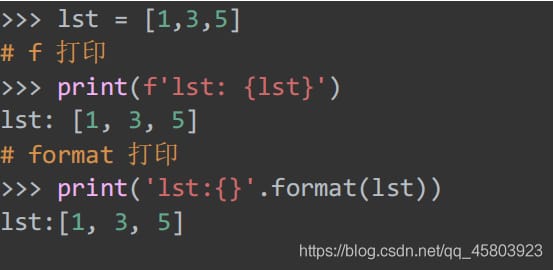
28. String formatting
Common uses of formatting strings
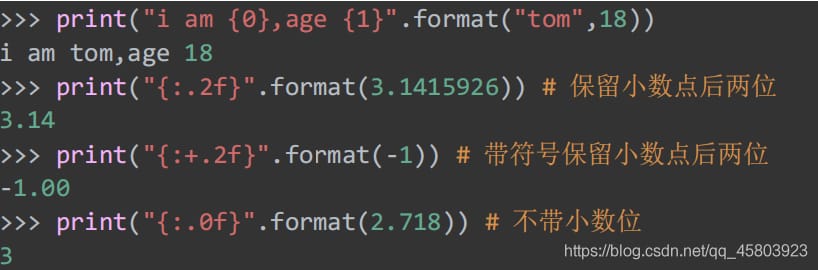
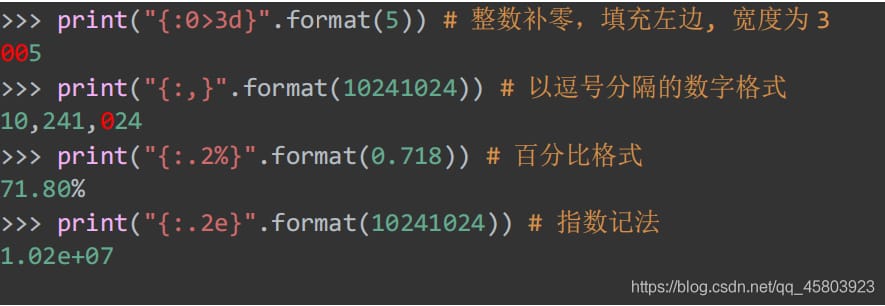
29. Return object hash values
Returns a hash of the object. It is worth noting that custom instances are hashable: the
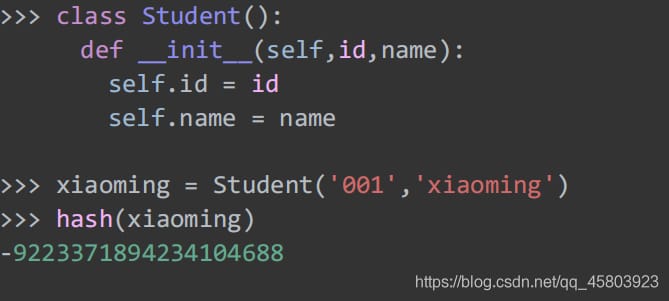
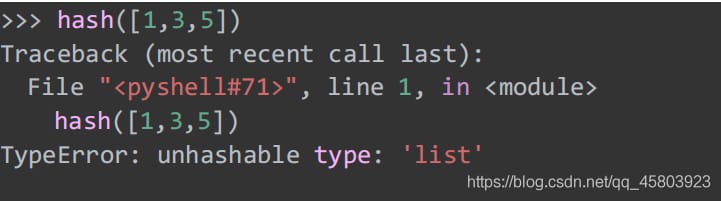
Variable objects such as lists, dict, sets, etc. are not hashable.
30. Open the file
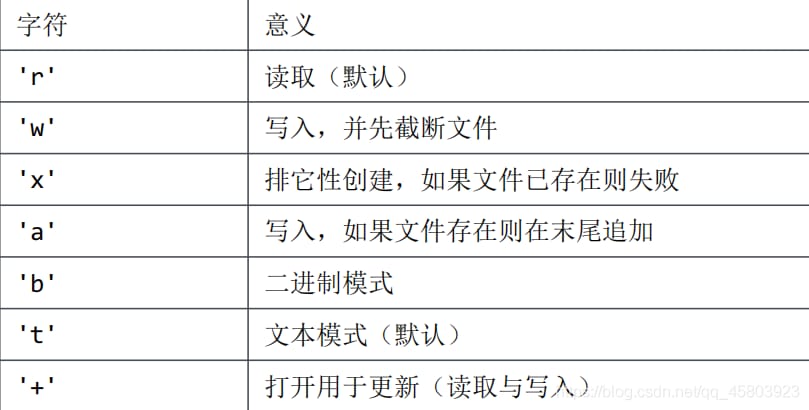
Return the file object
 mode Table of values.
mode Table of values.
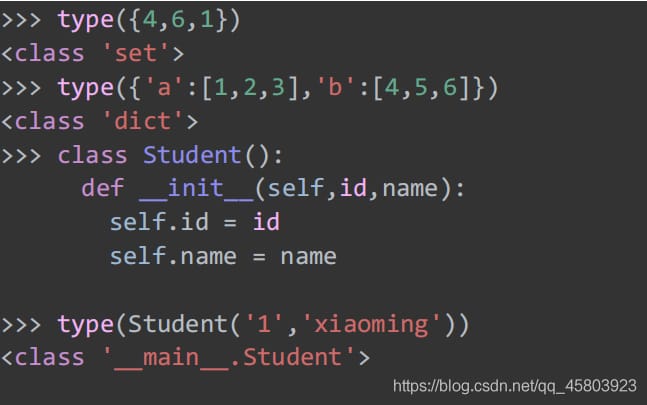
 31. View object types
class type(name, bases, dict)
31. View object types
class type(name, bases, dict)
Pass in the parameters and return the object type.
32. Two methods of creating attributes
Returns the property attribute, typically in the following way.
 Using class C.
Using class C.
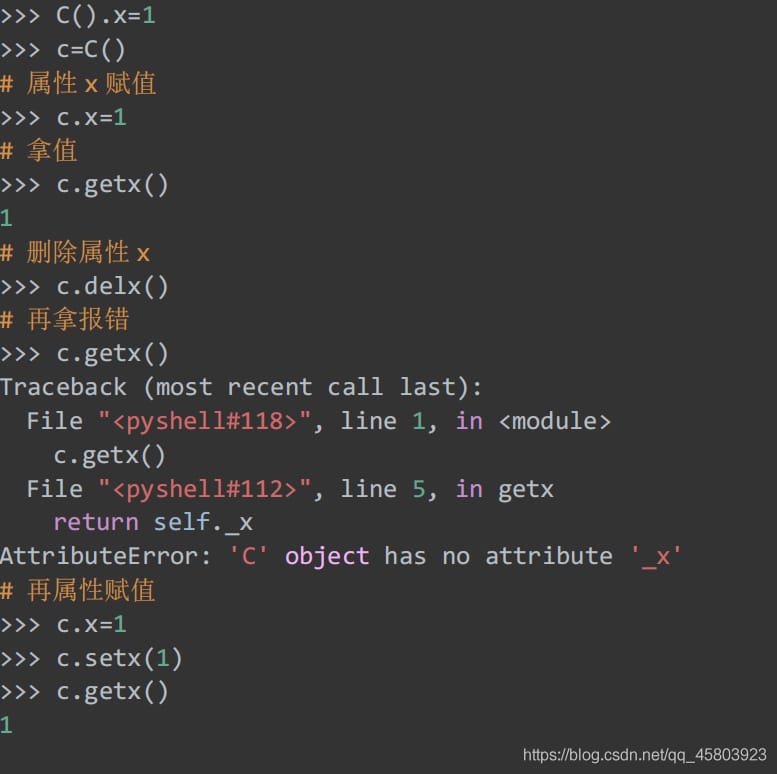
Using the @property decorator, achieve exactly the same effect as above.
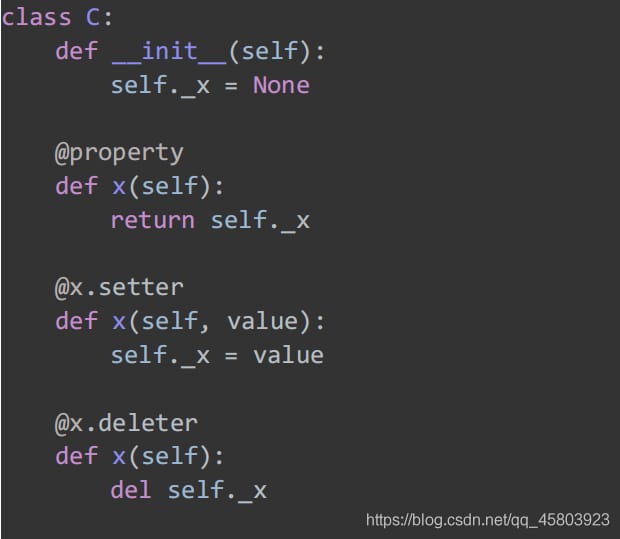
33. Is it possible to call
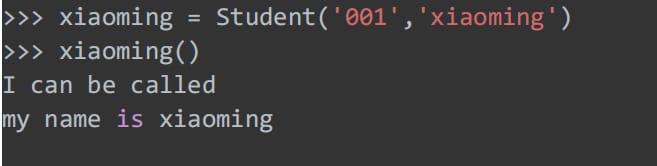
Determines if an object is callable, and a callable object is a callable object.

Student object instances are currently not available to call.
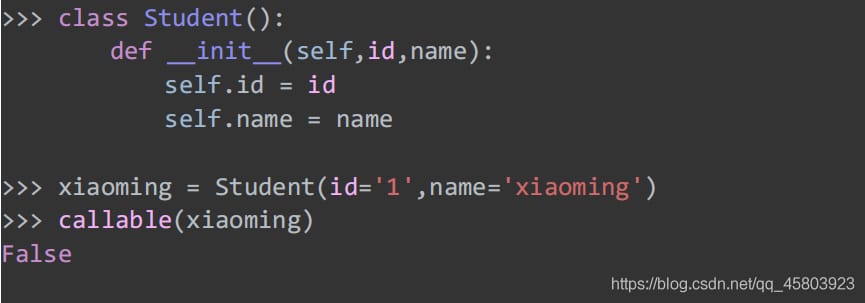
If xiaoming can be called , the __call__ method of the Student class needs to be overridden.
Call xiaoming() at this point:
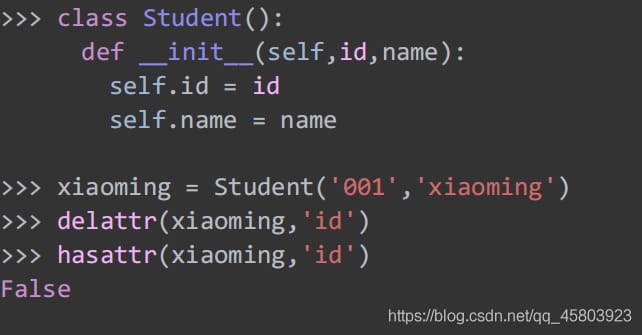
34. Dynamic deletion of attributes
Deleting an object's properties
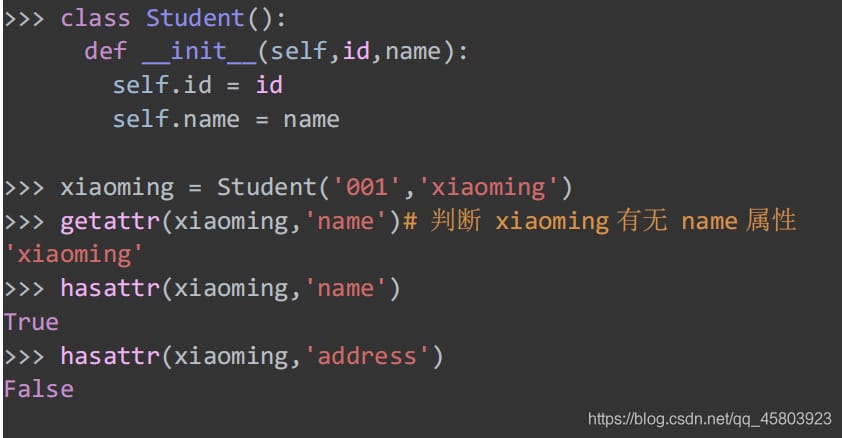
35. Get object properties dynamically
Get the properties of an object
 36. Whether the object has a certain attribute
36. Whether the object has a certain attribute
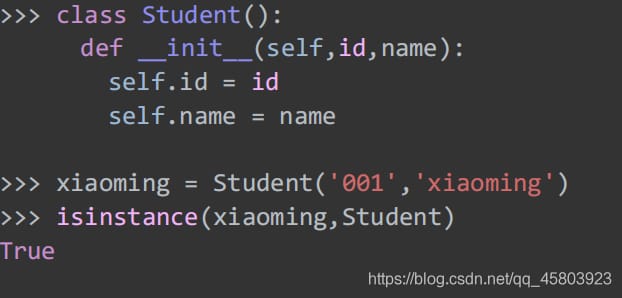
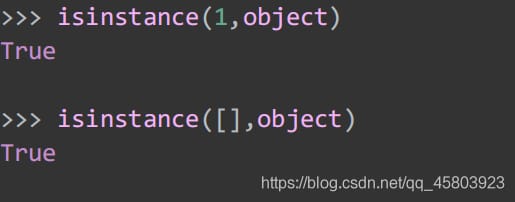
37.isinstance
Determines if the object is an instance of classinfo, and returns true if it is
 38. paternity identification
38. paternity identification
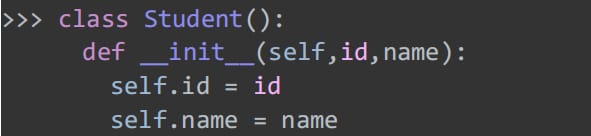
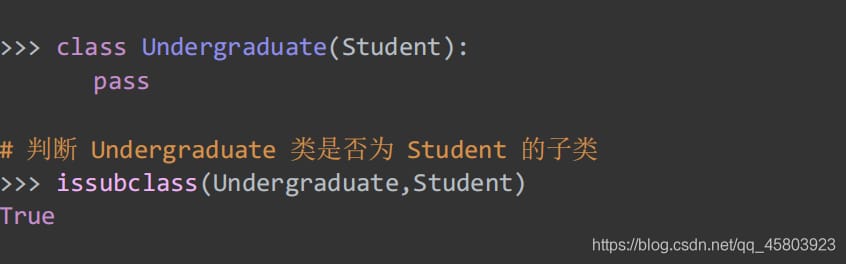 The second parameter can be a tuple.
The second parameter can be a tuple.
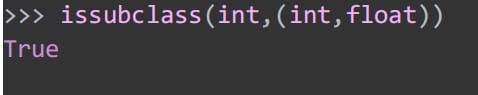
39. Root of all objects
object is the base class of all classes
40. One-click view of all methods of an object
Returns a list of variables, methods, and defined types in the current scope without arguments; with arguments, returns a list of properties and methods for the arguments.
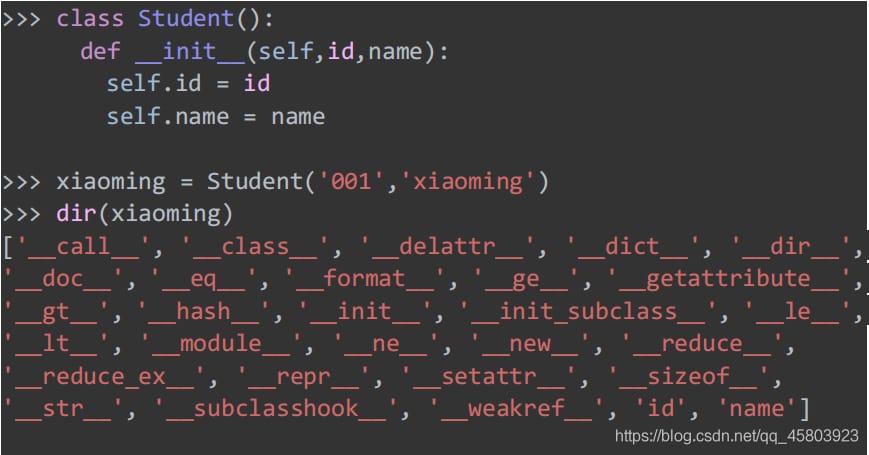
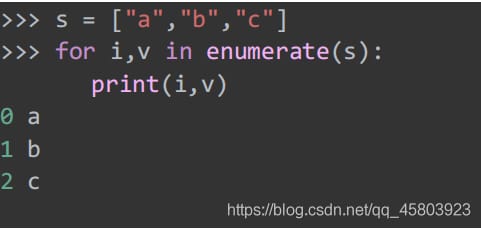
41. Enumerating objects
Python's enumeration objects

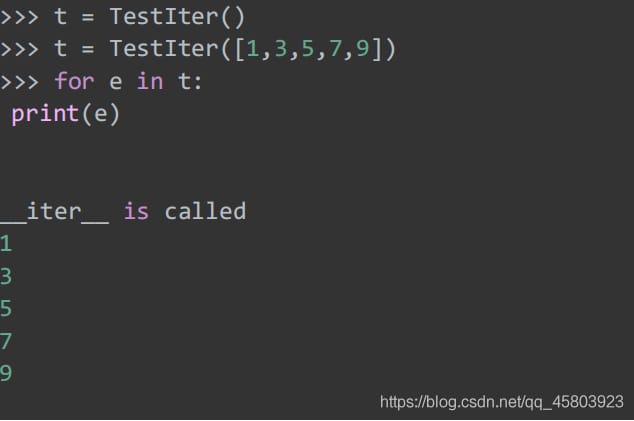
Iterate over the TestIter class.
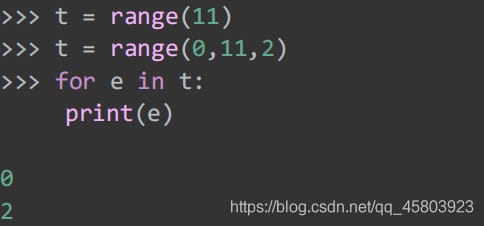
43. Creating range iterators
range(stop)
range(start, stop[,step])
Generate an iterator for an immutable sequence.

44. reverse
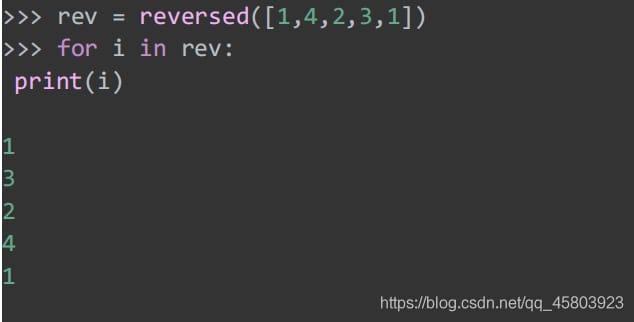
45. Packaging
An iterator that aggregates individual iterable objects.

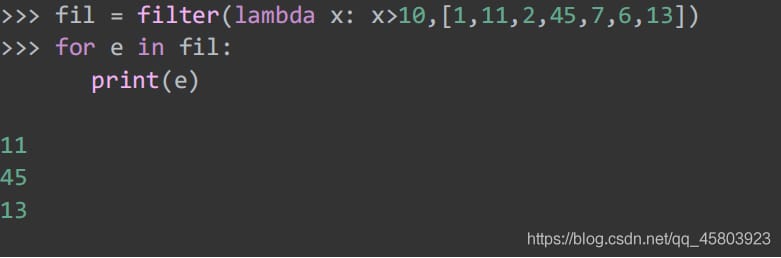
46. Filters
The function sets the filter by lambda expression, retaining the elements whose lambda expression is True.
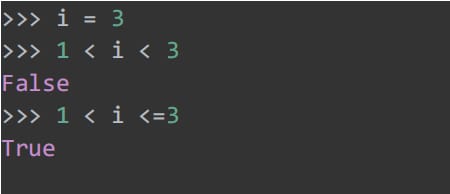
47. Chain comparison
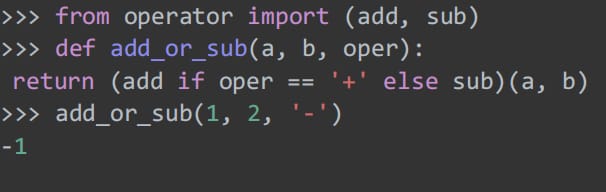
48. Chain operations
49.split Split Splitting
**
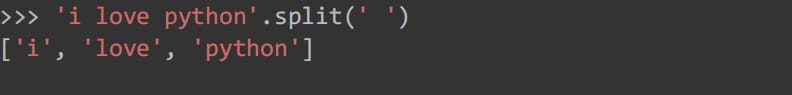
50.replace replace
 ls = line.strip('\n').split(',')
ls = line.strip('\n').split(',')
The strip() method is used to remove the characters specified at the beginning and end of a string (the default is spaces).
line.strip('\n') removes the newline character and returns a list.
split() slices the string by specifying the separator.
line.strip('\n').split(',') Slices the string by a comma.
#Personal public number yk 坤帝
#Background Reply Project 1 Get collation resources
f = open('sensor.txt','r',encoding = 'utf-8')
fo = open('earpa001.txt','w')
lines = f.readlines()
for line in lines:
ls = line.strip('\n').split(',')
if ls[1] == 'earpa001':
fo.write('{},{},{},{}\n'.format(ls[0],ls[1],ls[2],ls[3]))
f.close()
fo.close()
>>> int('12',16)
18
最新
-
nginxです。[emerg] 0.0.0.0:80 への bind() に失敗しました (98: アドレスは既に使用中です)
-
htmlページでギリシャ文字を使うには
-
ピュアhtml+cssでの要素読み込み効果
-
純粋なhtml + cssで五輪を実現するサンプルコード
-
ナビゲーションバー・ドロップダウンメニューのHTML+CSSサンプルコード
-
タイピング効果を実現するピュアhtml+css
-
htmlの選択ボックスのプレースホルダー作成に関する質問
-
html css3 伸縮しない 画像表示効果
-
トップナビゲーションバーメニュー作成用HTML+CSS
-
html+css 実装 サイバーパンク風ボタン
おすすめ
-
ハートビート・エフェクトのためのHTML+CSS
-
HTML ホテル フォームによるフィルタリング
-
HTML+cssのボックスモデル例(円、半円など)「border-radius」使いやすい
-
HTMLテーブルのテーブル分割とマージ(colspan, rowspan)
-
ランダム・ネームドロッパーを実装するためのhtmlサンプルコード
-
Html階層型ボックスシャドウ効果サンプルコード
-
QQの一時的なダイアログボックスをポップアップし、友人を追加せずにオンラインで話す効果を達成する方法
-
sublime / vscodeショートカットHTMLコード生成の実装
-
HTMLページを縮小した後にスクロールバーを表示するサンプルコード
-
html のリストボックス、テキストフィールド、ファイルフィールドのコード例